
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Storage: Accessing Data
|
|
|
|
The process of accessing data has 4 steps.
1. Seek
2. Rotate
3. Settle
4. Data transfer
| Step | Measured as: | |
| 1. seek move the read/write head to proper track | seek time (ms) | 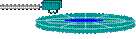
|
| 2. rotate rotate disk under the head to the correct sector | rotational delay (ms) | 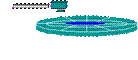
|
| 3. settle head lowers to disk; wait for vibrations from moving to stop (actually touches only on floppies) | settling time (ms) | 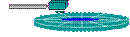
|
| 4. data transfer copy data to main memory | data transfer rate (kbit/s) | 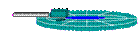
|
where ms stands for millisecond =.001 second and kbit/s is kilobits per second. Historically, one kbit has always been 1000 bits instead of 1024 bits. Go figure!
Total time to transfer a kilobyte:
| for floppies, | 175 - 300 ms |
| for hard drive, | 15 - 80 ms |
| new hard drives, (Jun. 2009) | .0032 ms (300 MB per sec). This is seriously fast!! |
Clearly, getting data from a hard disk is immensely faster than from a floppy.
Storage: Solid State Devices Solid state devices are currently the new hot technology for data storage. There are no moving parts. Data is stored electronically, not magnetically. Solid state drives replace traditional spinning-disk hard drives with banks of memory cards. Most SSDs use flash memory to store all those 1's and 0's in a way that keeps the data after power is off. Some SSDs use DRAM cards, the same as normal computer memory. The data vanishes once the power goes off.
Advantages:
- SSDs are super, super fast at reading and writing data.
- No moving parts to break.
- Does not need to be defragmented.
- Silent.
- Resistant to shock and vibration.
- Not affected by magnetic fields.
- Small size; light in weight.
- Uses less power than hard disk drives.
When a sector has had too many read/write cycles, the data becomes read-only and is written to a new area automatically. It's not lost!
| |
| Flash Memory |  Several different brands of removable storage cards, also called memory cards, are now available. These are solid-state devices (no moving parts) that read and write data electrically, instead of magnetically.
Devices like digital cameras, digital camcorders, and cell phones may use CompactFlash, SmartMedia, Memory Stick, or another flash memory card.
Laptop computers use PCMCIA cards, which are type of flash memory used as solid-state hard disks. Several different brands of removable storage cards, also called memory cards, are now available. These are solid-state devices (no moving parts) that read and write data electrically, instead of magnetically.
Devices like digital cameras, digital camcorders, and cell phones may use CompactFlash, SmartMedia, Memory Stick, or another flash memory card.
Laptop computers use PCMCIA cards, which are type of flash memory used as solid-state hard disks.
|
| USB drive |   This relatively new type of flash memory storage device does not yet have a generally accepted name. Each company calls it something different, including flash drive, jump drive, flash pen, thumb drive, key drive, and mini-USB drive.
All are small, at most about the size of your thumb or a large car key, but many are smaller. They plug into a USB port on the computer. No drivers are needed for recent versions of Windows. Plug it in and the computer reports a new drive!
Such small flash drives can have storage capacities from 8 MB to 128 GB or more!
Some flash drives include password protection and the ability to run software right off the USB drive. So cool!
The actual circuit board inside such a device is very small, so manufacturers add colorful and fun cases to get your business. This relatively new type of flash memory storage device does not yet have a generally accepted name. Each company calls it something different, including flash drive, jump drive, flash pen, thumb drive, key drive, and mini-USB drive.
All are small, at most about the size of your thumb or a large car key, but many are smaller. They plug into a USB port on the computer. No drivers are needed for recent versions of Windows. Plug it in and the computer reports a new drive!
Such small flash drives can have storage capacities from 8 MB to 128 GB or more!
Some flash drives include password protection and the ability to run software right off the USB drive. So cool!
The actual circuit board inside such a device is very small, so manufacturers add colorful and fun cases to get your business.
     The shiny metal parts in the center illustration are the contacts that must meet matching contacts on the computer. In the other devices those contacts are inside the rectangle-shaped connector.
The shiny metal parts in the center illustration are the contacts that must meet matching contacts on the computer. In the other devices those contacts are inside the rectangle-shaped connector.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 544; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!