
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
VII. Credit Policy
|
|
|
|
a) Supply the articles where necessary.
b) Write down 3-5 questions about the text.
c) Describe the principal instruments of credit policy.
Credit policy is____ component of economic policy. It is a combination of measures
taken by___ Central Bank to affect the supply of credit. The aims of_____ credit policy may
include stimulation or restriction of investment or consumer spending,________ avoidance of
price inflation (цінова інфляція).
Credit policy and monetary policy tend to be closely related and in some countries
credit policy is regarded as____ part of monetary policy.
Credit policy largely works indirectly. The Central Bank controls______ amount of credit
advanced (розміри кредиту, наданого) by commercial banks through the interest rate
policy, by influencing____ liquidity, expanding or contracting the volume of Central Bank
money. The principal instruments available for this purpose are __________ discount policy
(облікова політика), minimum reserve requirements and open market operations.
Direct credit control involving _______ establishment of credit ceilings (максимальний
156 PART III. BANKING


 розмір кредиту) is less frequently used now than in __________ past, many governments
розмір кредиту) is less frequently used now than in __________ past, many governments
regarding it as____ undesirable interference with the market mechanism.
VIII. Writing Practice. Give a short summary of the text "Central Banking System" Use the opening phrases from Appendix 1.
SECTION B. US Federal Reserve System
DISCUSSION 1. What do you know about banking system in the USA?
2. What American banks do you know?
reading US FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM
The Federal Reserve System (or Federal Reserve Board), commonly called Fed or the Federal Reserve, is the central bank of the United States. It was founded by Congress in 1913 to provide the nation with a safer more flexible, and more stable monetary and financial system. Over the years its role in banking and the economy has expanded.
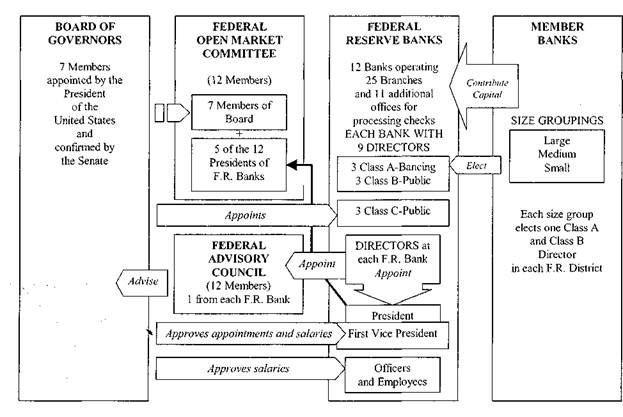
It consists of 12 Federal Reserve banks located in major cities (New York, Chicago, Boston, Dallas, Atlanta, San Francisco etc.) and a Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System located in Washington, D.C.
Members of the Fed's Board of Governors are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. However, the Fed maintains a degree of independence from both Congress and the executive branch. This is due in part to the governors' long terms of office - fourteen years. The Chairman of the Board of Governors is chosen by the President from among the seven board members and serves as chairman for four years.
Today the Federal Reserve's duties fall into four general areas:
• Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the money and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of full employment and stable prices.
• Supervising and regulating banking institutions to ensure the safety and soundness of the nation's banking and financial system and to protect the credit rights of consumers.
• Maintaining the stability of the financial system and containing systemic risk that may arise in financial markets.
• Providing certain financial services to the U.S. government, to the public, to financial institutions, and to foreign official institutions, including playing a major role in operating the nation's payments system.
The Fed performs three major functions:
• provides services to the banking system and the federal government,
• stabilizes the banking system, and
• controls the quantity of money in circulation.
UNIT 2. CENTRAL BANKS
ORGANISATION OF THE FEDERAL RESERVE SYSTEM
|
 The most important service of the Fed is cheque clearing, i.e. making sure that cheques written on one bank can be accepted at any other bank in the country.
The most important service of the Fed is cheque clearing, i.e. making sure that cheques written on one bank can be accepted at any other bank in the country.
The Fed performs a number of other services for banks and thrift institutions. It provides currency to banks and collects worn currency. It also provides safekeeping for securities.
Finally, the Fed performs banking services for the federal and foreign governments. It maintains US Treasury accounts from which all federal government payments are made. In addition, it assists in international transfers of funds by private firms and international agencies.
A second function of the Federal Reserve is stabilizing the banking system.
Banking panics often took place in the nineteenth century. Preventing such panics was the main reason for setting up the Federal Reserve System. With this in mind, the Fed was given broad powers to regulate banks.
The Fed's regulations are aimed at making sure that banks use sound business practices. For example, the Fed requires banks to hold a minimum fraction of their deposits as reserves.
The Fed was also given the power to supply extra reserves when needed. There are two ways in which the Fed can put reserves into the banking system. First, it can lend reserves to banks. Second, it can supply reserves to the banking system by buying government bonds from the public on the open market, in other words, by participating in open-market operations.
PART III. BANKING
 Despite its powers, the Fed failed to stabilize the banking system after the stock market crash of 1929. In the first years of the Great Depression many banks failed. As a result, a new agency, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), was set up in 1934 to give the system further stability. Fhe FDIC promises to pay depositors the full amount of their deposits, up to a limit, in the event that their bank fails.
Despite its powers, the Fed failed to stabilize the banking system after the stock market crash of 1929. In the first years of the Great Depression many banks failed. As a result, a new agency, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), was set up in 1934 to give the system further stability. Fhe FDIC promises to pay depositors the full amount of their deposits, up to a limit, in the event that their bank fails.
Today the Fed continues to regulate and stabilize the banking system but it has taken on another role as well, that of partner, with Congress and the executive branch, in the making of economic policy. The Fed's power as an economic policymaker comes from its ability to control bank reserves and, hence, to control the total amount of money in circulation.
The monetary policy of the Fed involves actions that affect its balance sheet (holdings of assets and liabilities).
The assets of the Fed are government securities and discount loans. The liabilities of the Fed are currency in circulation and reserves.
Liabilities. The two liabilities on the balance sheet, currency in circulation and reserves, are often called the monetary liabilities of the Fed. They are an important part of the money supply because increases in either or both will lead to an increase in the money supply (everything else being constant). The sum of the Fed's monetary liabilities (currency in circulation and reserves) and the US Treasury's monetary liabilities is called the monetary base.
Currency in circulation. The Fed issues currency. Currency in circulation is the amount of currency in the hands of the public (outside of banks). Currency held by depository institutions is also a liability of the Fed but is counted as part of reserves.
Reserves. All banks have an account at the Fed in which they hold deposits. Reserves consist of deposits at the Fed plus currency that is physically held by banks (called "vault cash" because it is stored in bank vaults). Reserves are assets for the banks but liabilities for the Fed because the banks can demand payment on them at any time and the Fed is obliged to satisfy its obligation by paying Federal Reserve notes.
Total reserves can be divided into two categories: reserves that the Fed requires banks to hold (required reserves) and any additional reserves the banks choose to hold (excess reserves).
Assets. The two assets on the Fed's balance sheet, government securities and discount loans, are important for two reasons. First, changes in the asset items lead to changes in reserves and consequently to changes in the money supply. Second, because these assets (government securities and discount loans) earn interest while the liabilities (currency in circulation and reserves) do not; the Fed makes billions of dollars every year - its assets earn income, and its liabilities cost nothing. Although it returns most of earnings to the federal government the Fed does spend some of it on 'worthy causes', such as supporting economic research.
Government securities. This category of assets covers the Fed's holding of securities issued by the US Treasury. The Fed provides reserves to the banking system by purchasing securities, thereby increasing its holdings of these assets. An increase in government securities held by the Fed leads to an increase in the money supply.
UNIT 2. CENTRAL BANKS
Discount loans. The Fed can provide reserves to the banking system by making discount loans to banks. An increase in discount loans can also be the source of an increase in the money supply The interest rate charged on banks for these loans is called the discount rate.
Extra facts:
• 'The Fed' dates back as far as 1907, when, during a financial crisis, J. P Morgan imported $ 100 million of gold from Europe to save the banks from bankruptcies.
• Over 41 million cheques are processed a day by the US Fed, averaging over 15 billion a year.
• The Federal Reserve Bank is the central bank of the United States. Unlike other central banks, it has several clearing houses.
VOCABULARY Board of Governors - Рада керуючих
NOTES soundness - надійність, міцність
worn - зношений safekeeping - зберігання to prevent - попереджувати, запобігати open-market operations - операції на відкритому ринку executive -виконавчий to deposit a check - депонувати чек balance sheet - балансовий звіт, баланс
assets - активи
liabilities - зобов'язання (пасиви)
discount loan - кредит з попередньо
виплаченими процентами
monetary base - грошова (монетарна)
база
vault cash - запас готівки в банку
obligation - зобов'язання
discount rate - облікова ставка, ставка
дисконту
 EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
1. What is the structure of the Federal Reserve System?
2. How are members of the Board appointed?
3. What functions does the Fed perform?
4. What services does the Fed perform for banks and government?
5. How does the Fed contribute to the stabilization of the banking system?
6. What role does the Fed play in the making of economic policy?
II. Find English equivalents for the following Ukrainian phrases: дворівнева банківська система займатися операціями на відкритому ринку чек,виписаний на банк депонувати чек Рада керуючих Голова Ради обирається
здійснювати кліринг чеків через Федеральну резервну систему вести рахунки купувати державні облігації.
III. Give derivatives of the following words:
important ad) intervene v choose v tend v
national ad] independent ad) maintain v represent v
function n governor n finance n stability n
supervise v executive ad] deposit n progress n
PART III. BANKING

 IV Choose the correct statement.
IV Choose the correct statement.
| 1. | a) The Federal Reserve System consists of state banks. b) The Federal Reserve System consists of Federal Reserve banks. c) The Federal Reserve System consists of national banks. |
| 2. | a) The Federal Reserve System does not affect the behavior of banks. b) The Federal Reserve System depends on the behavior of banks. c) The Federal Reserve System affects the behavior of banks. |
| 3. | a) The Federal Reserve System accepts deposits. b) The Federal Reserve System does not clear cheques. c) The Federal Reserve System clears cheques. |
| 4. | a) The Federal Reserve System sets the rules for how banks can operate. b) The Federal Reserve System does not set the rules for how banks can operate. c) In some cases the Federal Reserve System sets the rules for how banks can operate. |
| 5. | a) The assets of the Federal Reserve System are currency in circulation and discount loans. b) The assets of the Federal Reserve System are government securities and discount loans. c) The assets of the Federal Reserve System do not include government securities. |
| 6. | a) The liabilities of the Fed are currency in circulation and discount loans. b) The liabilities of the Fed do not include currency in circulation. c) The liabilities of the Fed are currency in circulation and reserves. |
| 7. | a) An increase in government securities held by the Federal Reserve System does not lead to an increase in the money supply. b) An increase in government securities held by the Federal Reserve System leads to an increase in the money supply. c) An increase in government securities held by the Federal Reserve System may lead to an increase in the money supply. |
| 8. | a) Nearly all banks have an account at the Federal Reserve System. b) All banks have an account at the Federal Reserve System. c) Some banks have an account at the Federal Reserve System. |
| 9. | a) Reserves are liabilities for the banks but assets for the Federal Reserve System. b) Reserves are assets for the banks as well as for the Federal Reserve System. c) Reserves are assets for the banks but liabilities for the Federal Reserve System. |
V The First Bank. Choose the best alternative to complete the text.
| 1. | a) association | b)agency | c) house | d) building |
| 2. | a) set | b) issue | c) series | d)lot |
| 3. | a) possessed | b) borrowed | c) owed | d) owned |
| 4. | a) Board of Directors | b) Court of Directors | c) Board of Governors | d) Executive Board |
| 5. | a) Governor | b) President | c) Director | d) Vice-President |
| 6. | a) branches | b) departments | c) divisions | d) subsidiaries |
| 7. | a) international | b) merchant | c) local | d) central |
| 8. | a) credit | b) fiscal | c) monetary | d) investment |
| 9. | a)bank | b) company | c) association | d) union |
| 10. | a) descendant | b) ancestor | c) heir | d) guarantor |
UNIT 2. CENTRAL BANKS
21 — 4-789
On the morning of July 4, 1791, a small brokerage (1)______ began selling shares in the
First Bank of the United States to the public. Within a few hours, the entire $8 million (2)
__ was sold. That fall, the stockbrokers met with representatives of the Federal
Government, which (3) ______ another $2 million in shares, and elected a (4) ___________.
Businessman Thomas Willing was chosen (5)_____, and the bank opened its main office in
Philadelphia. By the next spring, the bank was a going concern with (6)_________ in Boston,
New York, Baltimore and Charleston. Thus begun a successful 20-year enterprise and the
institution is now considered to be the nation's first (7)______ bank.
The First Bank was not a central bank in the modern sense - it didn't formulate (8)_______
policy, nor did it regulate banks. It was chartered by Congress to act as a commercial (9)
__ for a nation that had none, and also as the bank for a fledgling Federal Government
trying to establish itself financially. Still elements of central banking - and of America's
approach to central banking - emerged from the First Bank. Thus, it is unmistakably the
first American (10)____ to today's Federal Reserve System.
VI. Fill in the gaps with words from the box.
| central | securities | open market | Federal Reserve System |
| reserves | lender | regulate | commercial |
| operations | loans | financial | supply |
The United States had no central bank between 1836, when the Second Bank of the
United States ceased to exist, and 1913, when the (1)_______ was established. The impetus
behind the Federal Reserve was the need for a (2)_______ of last resort for the commercial
banks, to prevent (3) _____ panics. The system was devised after much study of (4)________
banks in other countries, particularly of their ability to (5)_________ the supply of credit by
adjusting the discount rate. Soon, however, the US banking authorities discovered that
they could regulate the (6)_____ of money and credit more easily through so-called open-
market (7)____, that is, through buying and selling federal government (8)_______ in the (9)
__. When the Federal Reserve System sells securities, the reserves of the (10)________ banks
are reduced, and consequently their ability to make (11) ________ is decreased. When the
Federal Reserve System buys securities, the opposite effect is achieved: the (12)________ of
the banks are increased, and correspondingly their ability to make loans.
VII. The Federal Reserve System. Complete the article using the words in the box.
| Senate | accumulation | feature | nations |
| office | safeguard | controlled | gold vault |
| constituted | governors | central | gold reserves |
| consists | President | regulate | pressures |
The Federal Reserve System is the (1)_____ bank of the USA and (2)_____ of 12 national
banks spread across the country. It is (3) _______ by a board of seven (4) ______ who are
appointed by the (5)_____ and confirmed by the (6)______. Terms of (7)_____ last fourteen
years to insulate Governors from political (8)_______. The most important function of the
Federal Reserve System is to (9)_____ the supply of money and (10)____ the position of the
currency. The most popular (11) _____ of the Federal Reserve Bank is the (12) ________, a
massive underground safe under Manhattan. It contains the largest known (13)_________ of
gold in the world. The gold (14)______ about one-third of the (15)_____ of the world's non-
communist (16)___.
VIII. Writing Practice. Make a short summary about assets and liabilities of the Fed from the text "US Federal Reserve System" Use the opening phrases from Appendix 1.
PART HI. BANKING

 SECTION C. Bank of England.
SECTION C. Bank of England.
DISCUSSION 1. What do you know about British banking system?
2. What British banks do you know?
reading BANK OF ENGLAND
The Bank of England is Britain's central bank. Established privately in 1694 and chartered by the government in return for a loan, it is the world's second oldest central bank, being six years younger than Sweden's Riks-bank, Although started as a private bank it gradually evolved into a Central Bank. Its original purposes and functions were very different from its present ones. It started as a commercial bank with private shareholders and developed a large private banking business. Today it serves as the banker to the government of the United Kingdom with sole authority to issue notes in England and Wales and also as the banker to the country's commercial banks. It was privately owned until it was nationalised in 1946 but it had long governed its operations in the national interest.
The Bank of England is controlled by a Court of Directors made up of the Governor, Deputy Governor and 16 Directors. They are all appointed by the sovereign on the recommendation of the Prime Minister. Governors serve for term of five years, and Directors for four years: both can be renewed. Twelve of the directors are part-time and are chairmen of large public companies or banks. Traditionally one director is the General Secretary of a major trade union. The Court meets every Thursday in the Court Room.
From its founding in 1694 it acted as the government's banker lending it money to fund the National Debt. It soon acquired a practical monopoly of the note issue, eventually other banks began keeping deposits with the Bank of England and using it as a clearing house for their transactions with one another. After the Bank Charter Act of 1844 the Bank of England had become a banker to other banks and to government. It had also acquired another function associated with central banking - that of being the 'lender of last resort' to which other banks could turn for aid when they were hard pressed.
During the 19th century the Bank of England developed techniques for regulating interest rates and the amount of credit issued by itself and by the banking system generally. As the leading bank in the world's leading financial center its actions were considered critical in maintaining the international gold standard. By adjusting its discount rate, that is, the interest it charged on loans to commercial borrowers, it was able to affect the international flow of short-term capital. An increase in the discount rate would attract money to London and at the same time discourage borrowers, a reduction in the discount rate would have the opposite effect.
Nowadays the Bank of England is both monetary authority and bank supervisor, it is charged with the control of the banking system in the interests of the nation. The chief functions of the Bank of England are to act as
UNIT 2. CENTRAL BANKS 163
21 *
 the Government's bank in the widest possible sense. The main Government account is the central Exchequer Account in the Bank to which all Government revenues eventually are credited and from which all Government payments originate. Other major ministerial accounts also are kept in the Bank and the major expenses of Government departments are disbursed from these accounts.
the Government's bank in the widest possible sense. The main Government account is the central Exchequer Account in the Bank to which all Government revenues eventually are credited and from which all Government payments originate. Other major ministerial accounts also are kept in the Bank and the major expenses of Government departments are disbursed from these accounts.
The Bank does not lend money to the Government. If the Government needs funds it borrows the sums required by issuing Treasury bills or by selling stocks. Treasury bills are short-term securities offered for sale by tender and repayable three months after issue. The Bank's function is to balance every day the sums received against the sums needed never allowing idle balances to. accumulate. If money is received in excess of requirements the Bank buys back Treasury bills adding them to its portfolio.
The Bank of England is a banker to the commercial banks and also to the discount and accepting houses. The ordinary commercial banks keep about half of their cash assets on current accounts with the Bank of England, which therefore acts as the 'Bankers' Bank' using these deposits for the day-to-day settlement of indebtedness between the banks. A lot of overseas central banks and international bodies have accounts with the Bank of England to facilitate a wide variety of international transactions and to promote trade and prosperity.
The Bank is the central note-issuing authority. New notes are issued and worn notes are withdrawn in very large numbers every day.
The Bank performs registration activities as registrar of government stocks and stocks of nationalized industries. It also pays dividends when they fall due.
The Bank acts as the Government's agent for the administration of exchange control and protects the gold and foreign exchange reserves.
Being monetary authority in the country the Bank implements the Government policy in the money market and the loan market by raising or lowering Bank Rate.
Because of its influential position in the financial affairs of the country the Bank gives useful financial advice to the Treasury to assist it in forecasts of the economic situation and the balance-of-payments position. The Bank also advises companies on capital structure and finance.
The style of work of the Bank is much admired by the world and gives the credit for the safe and successful growth of London as the world's number one international banking centre.
VOCABULARY sovereign - монарх registrar - реєстратор, реєстраційне
NOTES to charge (with) - тут доручати бюро
Exchequer - Казначейство to fall due - наставати (про термін
to disburse - оплачувати (з державних платежу)
коштів) exchange control - валютний контроль
sale by tender - продаж на торгах Bank Rate - ставка центрального банку
idle - тут вільний, невикористаний
discount house - обліковий банк
accepting house - акцептний банк
settlement of indebtedness -
урегулювання заборгованості
PART III. BANKING
 EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
EXERCISES I. Answer the following questions:
1. What were the original purposes and functions of the Bank of England?
2. What are the functions of the Bank of England?
3. What does 'lender of last resort' mean?
4. Who controls the Bank?
5. In what areas of monetary policy is the Bank of England involved?
II. Foundation of the Bank of England. Complete the text by choosing the best alternative
| 1. | a) political | b) financial | c) monetary | d) investment |
| 2. | a) plans | b) prospects | c) projects | d) schemes |
| 3. | a) backed | b) helped | c) supported | d) provided |
| 4. | a) grant | b) loan | c) credit | d)advance |
| 5. | a) Governor | b) Director | c) Manager | d) Head |
| 6. | a) foreign | b) central | c) joint-stock | d) clearing |
| 7. | a) assets | b) capital | c) funds | d) liabilities |
| 8. | a) contribution | b) membership fee | c) crediting | d) subscription |
| 9. | a) British Debt | b) National Debt | c) British Banking | d) National Capital |
| 10. | a) activity | b) transactions | c) operations | d) business |
| 11. | a) Court of Directors | b) Board of Directors | c) Court of Managers | d) Executive Board |
| 12. | a) opening | b) creation | c) foundation | d) nationalisation |
The revolution of 1688, which brought William and Mary to the throne, created a
degree of political stability unknown for nearly a century and unleashed a wave of (1)______
experimentation. Numerous (2)_____ for a national bank were mooted {обговорювати)
including a proposal for a Bank of England from a Scotsman, William Paterson. A colourful figure and an inveterate (завзятий) promoter of financial projects, Paterson,
(3)___ by a powerful group City group, proposed a (4)________ of 1,200,000 pounds to the
government at 8% interest, in return for which the subscribers to the loan would be
incorporated as the (5)____ and Company of the Bank of England, the first (6)______ bank
in the country. The government, increasingly desperate for (7)_______ to wage a war against
France that has begun in 1688, supported the scheme and secured parliamentary
approval. The (8)____ to the Bank's capital proved highly popular and the money was
raised in less than three weeks. It marked the beginning of the funded (9)_______.
The Charter was sealed on 27th July 1664 at Powis House, Lincoln's Inn Fields and the
Bank opened for (10)____ a few days later in temporary accommodation at the Mercers'
Hall in Cheapside with a staff of just seventeen clerks and two gatekeepers. The (11)_______
responsible for the management of the Bank was headed by the Governor, Sir John Houblon, grandson of a French Protestant refugee and a prominent Threadneedle Street merchant; Paterson was, for a brief period, a Director. The first notes to hear the name of
the Bank of England appeared very shortly after its (12)______. In 1734 the Bank moved to
the new building, arguably the first purpose-built bank in the world, in the Threadneedle Street.
III. The Bank of England Complete the article using the words in the box.
| borrowings | customers | central | assists |
| reserves | commercial | payments | shareholders |
| national debt | cover | founded | clearing |
| institutions | bullion | operational balances | services |
UNIT 2. CENTRAL BANKS 165
(1)___ in 1694 the Bank of England is one of the oldest banking (2)_______ in the world.
It started as a (3) _____ bank with private (4) ______ but also arranged (5) ______ for the
government. The Bank of England offer a similar range of (6)________ to any other bank.
There are three important groups of (7)______: the commercial banks, other (8)_____ banks,
and the Government. All the (9)_____ banks keep accounts at the Bank of England.
The banks are obliged to keep (10)______ large enough to (11)_____ their needs. Other
central banks keep accounts and gold at the Bank of England and conduct foreign
exchange and (12) ____ business through the bank. The Government keeps its main
banking accounts at the Bank of England in order to receive and make (13)_________. The
bank manages the UK's (14)______ of gold and foreign exchange, arranges Government
borrowing and (15)____ in managing the (16)____.
IV What do you know about the Bank of England? Which of the following statements are true or false:
1. The Bank of England is one of the oldest central banks.
2. The Bank of England was established to finance the Napoleonic Wars.
3. The Bank of England started as a nationalised company.
4. A well-known forger advised the Bank of England how to stop forgers during his time in prison.
5. Poland was the first European country to have a woman governor of the central bank.
6. The Bank of England destroys 60 million pounds a month.
7. The governor of the Bank of England from 1898 to 1908 wrote a famous children's story.
8. Only two bars of gold kept in the Bank of England actually belong to the bank.
9. The Bundesbank is controlled by the European Community.
10. The Bank of England was privatised in 1975.
11. When a company is brought into state ownership it means that it leaves the private sector.
12. The Bank started issuing notes after the Second World War.
V The Role of Government and the Central Banks. Complete the text using the words in the box.
| demand | value | foreign |
| stability | exchange | interest |
| intervention | ERM (Exchange Rate Mechanism) | policy |
The authorities have a number of means of influencing the (1)_______ rate. The Bank of
England can intervene in the (2)_____ exchange market by buying or selling pounds. This
acts directly on the (3) _____ for or supply of sterling. In addition, news of the Bank's
operations, if detected by the market, can convey a message as to the government's
overall stance on exchange rate (4) ______ and may generate supporting deals from the
market which can magnify the effect of (5)_____. However, although intervention can be
effective in smoothing short-term fluctuations in the (6) ________ of the pound, it cannot
resolve underlying economic problems, which may need to be addressed by other
measures, such as altering the level of (7)_______ rates. Although such decisions are now
taken within the framework of (8)______ membership, the overall objective of monetary
policy in the UK remains the achievement of domestic price (9)______.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-23; Просмотров: 1128; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!