
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Word Order
|
|
|
|
Grammar Study
Ex. 28. Make up short dialogues using the expressions from Ex. 25.
CTB: You are welcome.
CTB: Ok, Mr. Curtis. I’ll put that in the mail for you.
Caller: Thanks.
e.g.: - Can I help you?
- Could you give me some information about travelling abroad, namely to Turkey, please?
- Certainly.
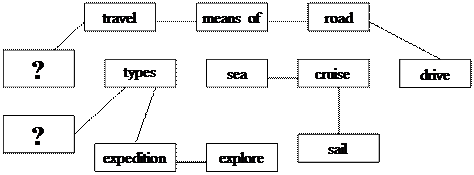
Ex. 29. Study the network and enlarge it. Make sentences according to the models.
e.g. Cruise is a type of travelling when you sail in the sea.

Ex. 30. Look at the prompts below. Make sentences using correct verb forms, articles, prepositions, plurals. Come back to the text in Ex. 19, and check yourself.
e.g.: Many people go abroad to spend their holidays.
| Verbs | Nouns | ||
| stay rent prefer spend lie enjoy use protect visit | look dine take choose learn get to know discover listen meet | holiday places villa tent change of scene things way life people | restaurants art galleries shop windows apartment campsite food rhythm museums |
SENTENSE PATTERN:
1. Normal sentence pattern in English is following. The main members of a sentence are subject and predicate:

2. Subject is the agent of the sentence in the active voice: it is the person or thing that does the action of the sentence, and it normally precedes the predicate.
Note: Every sentence in English must have a subject, except commands and exclamations. The subject may be a phrase or a group of words ending with a noun.
e. g. The book is on the table.
That new, red car is at his house.
3. Predicate (or verb) follows the subject. It generally shows the action of the sentence.
Note: Every sentence must have a verb. The verb may be a single word or a verb phrase. A verb phrase may consist of one or more auxiliaries and one main verb. The auxiliaries always precede the main verb or the verbal.
e. g. John drives too fast. John doesn't drive too fast.
John is driving too fast now. John was to drive too fast.
Jane has been reading that book for hours. John was driven to his place.
4. It is better to begin analyzing the sentence with the predicate because it is not often difficult to find it in the sentence. Some forms of verbs always show the beginning (starting point) of the predicate. Then you should analyze the subject which is located before the verb.
Clear beginning of predicate or predicative group:
a) forms of be: am, is, are, was, were, will be, shall be, would be, should be;
b) forms of have: have, has, had, will have, shall have, should have, would have;
c) forms of modal verbs and auxiliaries: can, could, may, might, must, should, ought to, need, needed, dare, dared, will, would, shall, do, does, did.
Ex. 31. Find the subject (a) predicate (b).
a) 1. We girls are not going to the country.
2. The weather was very bad yesterday.
3. Henry and Marcia have visited the president of the company.
4. The boy in the corner is my friend.
5. The American Declaration of Independence was drawn up in 1776.
6. No one in the Spanish class knew the correct answer to Mr. Perez’s question.
7. The Statue of Liberty was a gift of friendship from France to the United States.
b) 1. She must have gone to the seaside resort.
2. The place is extremely dangerous.
3. It was raining at 6 o’clock last night.
4. Trees grow.
5. She enjoyed the voyage round Europe.
6. I would like to visit a lot of places.
7. Athletes should follow a well-balanced diet.
8. On our trip to Spain we crossed the Atlantic Ocean.
Ex. 32. Point out the beginning of the predicate group (verb phrase). Say how many clauses there are in each sentence.
1. That political science class is taking a trip to Russia in spring.
2. While we were in Alaska, we were trying to find an Eskimo village.
3. After Henry had visited Italy and France, he was going to visit Switzerland.
4. If either of us has taken a holiday, we will not be able to finish the work.
5. Mr. Jones accompanied by several members of the committee has proposed some changes of the rules.
6. The northern-west health resort is to be founded in Siberia, on the banks of the Lena River – it is being under construction now.
7. It is certain that if sailors had had no compass they would not have traveled all over the seas and oceans.
8. Whether you are crossing the Channel or Sahara, going away for a few days, our travel service will meet your needs.
9. If you have any questions you can visit or telephone any of the Branches of Foreign and Travel Services and a member of the staff will be pleased to help you or they can arrange for you to discuss your requirements with an appropriate person.
10. The Japanese visitors do like to see evidence of high level of security, especially with so many ladies travelling unaccompanied; so relevant information could be provided in room literature and promotional leaflets.
Ex. 33. Put the words into the right order.
1. In the country-side / like to spend / many people / their days off.
2. To discover new things / it / always / different ways of life / interesting / is / and.
3. The sons / traveled / in the 17th centuries / of British aristocracy / throughout Europe / to improve their knowledge.
4. Before the Second World War / didn’t ever go away / almost all / on holiday / of the population / at all.
5. Travellers / under / the World Tourist Organization / various heading / classifies.
6. The footpaths / the growing number / is damaging / of the palace / of visitors / in the garden.
7. Take / of the sights / a camera / most travelers / pictures / and / with them / to have / of a city / holiday-makers.
8. Travelling / the place / long time / doesn’t / of / to /take / destination.
Ex. 34. Put the words into the right order.
1. I / in / for / lived / years / Paris.
2. He / years / overseas / has to / travel /every/ five.
3. We / Tansania / ten / ago / were / in / years / about.
4. His / into / of / the / waters/ in / 14 / dropped / Spanish tourist / the Loch Ness / wallet / years / Scotland / Gaspar Sanches / ago / the.
5. Would / a / in / industry / she / job / like / the / tourist / find / to.
6. Fairy-tale / to / the / stroll / Czech State / through / the / of / visitors / streets / millions / Prague / of.
7. All / for / history / traveled / over / throughout / people / have /variety / of / world / purpose/ the.
8. This / only / people / had / and / rich / until / very / in / /free / century / time / to / the / outside / area / money / local / society / travel / own / their.
9. By / a / day's / the /the / 1870s / family / was / trip / typical / to / a / holiday / seaside.
Ex. 35. Read the text and point out the subjects and the predicates, translate them.

 Throughout history, people have been travelling all over the world for variety of purposes. However, it is only in the last fifty years that people have travelled in such huge numbers for pleasure. Until this century only very rich and leisured people in society had free time and the money to travel outside their own local area. For example, it is known the wealthy Romans went to seaside resorts in Greece and Egypt. In the 17th century the sons of the British aristocracy travelled throughout Europe to improve their knowledge. With the railways and the industrial revolution in Britain working-class people began to travel. By the 1870s a typical family holiday was a day’s trip to the seaside. A century later during the 1970s the advent (= появление) of the cheap package holiday resulted in many people being able to enjoy the sun, beaches and food in any hot country. Growing affluence (= богатство), faster planes and improved facilities have meant that more and more people travel abroad every year and now people have begun to travel further afield (= все дальше и дальше).
Throughout history, people have been travelling all over the world for variety of purposes. However, it is only in the last fifty years that people have travelled in such huge numbers for pleasure. Until this century only very rich and leisured people in society had free time and the money to travel outside their own local area. For example, it is known the wealthy Romans went to seaside resorts in Greece and Egypt. In the 17th century the sons of the British aristocracy travelled throughout Europe to improve their knowledge. With the railways and the industrial revolution in Britain working-class people began to travel. By the 1870s a typical family holiday was a day’s trip to the seaside. A century later during the 1970s the advent (= появление) of the cheap package holiday resulted in many people being able to enjoy the sun, beaches and food in any hot country. Growing affluence (= богатство), faster planes and improved facilities have meant that more and more people travel abroad every year and now people have begun to travel further afield (= все дальше и дальше).
(English for International Tourism)
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-03-31; Просмотров: 963; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!