
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Syntactic roles of prepositional phrases
|
|
|
|
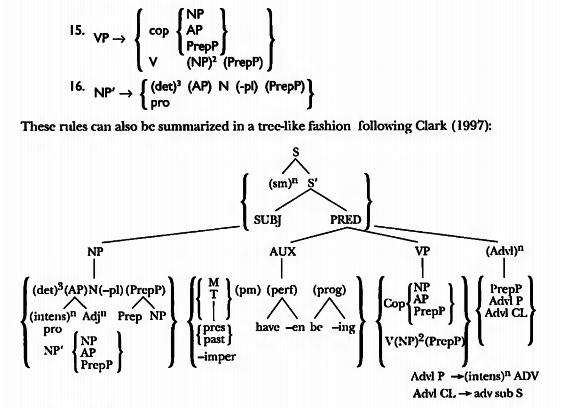
Perhaps the most widespread constituent that we have introduced in our phrase structure rules is the prepositional phrase (PrepP). Prepositional phrases can be generated as parts of noun phrases, verb phrases, adjective phrases, adverbials, or object noun predicates:
PrepP in NP: a man of honor, an ounce of vodka
PrepP in VP: be in the house, give the book to Mavis
PrepP in AP: fond of cats
PrepP in advl: do laundry on Saturday
PrepP in object noun predicate: put the flowers on the table
The three structures with prepositional phrases that are most difficult to distinguish structurally are those where the PrepP is part of the verb phrase, those cases where the PrepP functions as the object noun predicate, and those cases where the PrepP is generated after the verb phrase as an adverbial modifying the whole sentence.
We are going to generate prepositional phrases under the verb phrase only in the following cases:
1. where the PrepP follows the copular verb be and predicates something of the subject NP, such as:
John is in his room.
2. where the PrepP is needed to complete the argument structure of a verb. For example:
a. intransitive verb: The baby lay in the crib.
b. ditransitive verb: Sue handed the letter to Mr. Blake.
Other verbs like lay are lurk, live (= reside), head (= set out for), and arrive. The verbs come and go are also of this type; however, the adverbial (often a PrepP) is frequently not explicitly stated because it is understood from the context. Some other verbs like hand are give, tell, explain, send, transfer, show, and deliver. We normally generate PrepP as the object noun predicate only with verbs like put, place, set, or stand and verbs like elect and consider when they are followed by as:
We put the vase on the table.
We elected Tim as the chairman.
Again, what distinguishes object noun predicates from other object-like constituents is that they predicate something of the direct object The vase is on the table; Tim is the chairman.
All other cases where the PrepP follows the verb are adverbial in origin and are generated under the adverbial node (Advl):
Mrs. Symms teaches kindergarten in Dallas.
Jack sells auto parts for a living.
We canceled the picnic after the thunderstorm.

|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-04; Просмотров: 738; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!