
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Static characteristics of DC series excitation electric motor in braking modes
|
|
|
|
Motor
Static mechanical characteristics of DC series excitation electric
Normal scheme of powering of DC motor with series excitation is shown on the next figure.

There are next designations on the scheme:
Ia – is an armature current;
Iexc – is an excitation current;
Raa – is an additional resistance in armature circuit.
As opposed to DC motor with independent excitation magnetic flux Ф
here is a function of armature current, since excitation winding LM is in series with armature winding, i.e.  , because magnetic flux is a load function, as
, because magnetic flux is a load function, as  .
.
On the other hand, dependence of magnetic flux from armature current is a magnetic characteristic  (magnetization curve), see the figure.
(magnetization curve), see the figure.
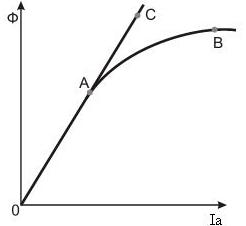
Since magnetization curve is nonlinear characteristic and there is no exact analytic expression of it that is why it is difficult to obtain an exact analytic expression for mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation, as opposed to DC motor with independent excitation.
To obtain approximate analytic expression for mechanical characteristic it should be neglected by nonlinear dependence, by which current 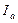 and magnetic flux
and magnetic flux 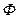 are connected, (consider, that this dependence is linear), i.e. real dependence OAB in figure, shown above, we will change by idealized dependence represented by straight line OAC. By physical essence it means, that motor steel has infinite magnetic permeability μ, i. e. steel remains unsaturated at any current values.
are connected, (consider, that this dependence is linear), i.e. real dependence OAB in figure, shown above, we will change by idealized dependence represented by straight line OAC. By physical essence it means, that motor steel has infinite magnetic permeability μ, i. e. steel remains unsaturated at any current values.
Even with this assumption analytic expression for mechanical characteristic will be rather complex.
This expression can be obtained in such a way. At linear dependence 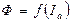 , this dependence can be written as:
, this dependence can be written as: 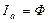 , i. e.
, i. e.
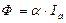 , (3.21)
, (3.21)
where 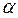 - is a proportional factor between
- is a proportional factor between 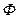 and
and 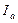 .
.
Basing on (3.21), expression for the moment will have the next view:

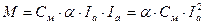 (3.22)
(3.22)
where  and
and 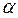 are constant values.
are constant values.
In general view equation of electromechanical characteristic of DC motor is known as:
 (3.23)
(3.23)
Substituting in the equation (3.23) the value of magnetic flux from (3.21) we obtain:
 (3.24)
(3.24)
Equation (3.24) is representing as the dependence , i. e. it is the electromechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation.
, i. e. it is the electromechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation.
From equation (3.22) the value of the current (for motor mode) will be the next:
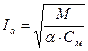 (3.25)
(3.25)
Substitute the value of armature current from (3.25) in the equation (3.24) and we will obtain:
 (3.26)
(3.26)
Equation (3.26) is representing as the dependence , i. e. it is the mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation. Mathematical interpretation of this expression represents a hyperbolic curve of the next view:
, i. e. it is the mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation. Mathematical interpretation of this expression represents a hyperbolic curve of the next view: 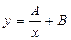 .
.
Thus, for unsaturated DC motor with series excitation mechanical characteristic has hyperbolic dependence for which coordinate axis is an asymptote.
The high slope in the limits of low moment (current) values is the feature of mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation. It is explained by dependence of the speed not only from voltage drop in armature circuit (as in DC motor with independent excitation), but also from changing of magnetic flux at current changing, especially at low current values.
Equation (3.26) gives only general representation about mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation. At computations it is undesirable to use this equation, because DC machine with unsaturated magnetic system almost is not constructing. Because of the reason, that real mechanical characteristics of DC motor with series excitation are substantially differ from characteristics, expressed by equation (3.26), the construction of mechanical characteristics is had to do by grapho-analytical methods with the help of catalogue data, where natural characteristics of DC motor with series excitation  and
and  are given.
are given.
For industrial and special types of DC motor with series excitation these characteristics are valid for any motor of given type, because these characteristics are given at relative units 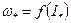 and
and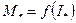 .
.

Taking into account mentioned above, mechanical characteristic of DC motor with series excitation has the view, shown on the figure, where:
- characteristic 1, constructed for linear dependence 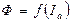 , i. e. corresponding to equation (3.26);
, i. e. corresponding to equation (3.26);
- characteristic 2 – is real natural characteristic, constructed by grapho-analytical method with taking into account saturation of magnetic system, it has a part 2′, where dependence is almost linear. It is explained by those facts, that hyperbolic dependence can exist at low load current (area AB), when magnetic system is unsaturated yet, but at great loads, when magnetic flux becomes almost constant because of substantial saturation, mechanical characteristic has almost linear character (area BC).
Mechanical rheostat characteristics are constructed only by grapho-analytical or graphical methods and have the next view
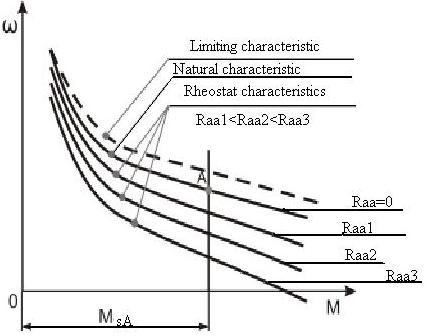
With decreasing of armature circuit resistance characteristic stiffness is reduce (at the same static moment of resistance the speed decreases). It is explained by those facts, that with decreasing of armature circuit resistance increases the voltage drop in it, because the speed decreases.
From equation (3.26) it is seen, that at tending of moment (current) value to zero  (i. e. at ideal open circuit) the motor speed tends to infinity
(i. e. at ideal open circuit) the motor speed tends to infinity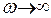 .
.
Unlimited increasing of speed at approaching to ideal open circuit doesn`t exist in reality. It is conditioned by the next conditions:
- presence of mechanical losses in open circuit(friction in bearings, bushings, by area and so on);
- presence of residual magnetic flux independently of armature current.
But at open circuit the speed is rather high and achieves .
.
Such increasing of speed in real conditions is not permitted because of two reasons:
- limit of mechanical strength of motor rotating details, at first, of the commutator and bands;
- abrupt commutation worsening at high speed because of increasing  (emf at switching), which can result to ring fire.
(emf at switching), which can result to ring fire.
At these conditions standards allow in real DC motor with series excitation speed excessive not more than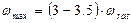 .
.
On the other hand - DC motor with series excitation is prohibited to operate in conditions, which allow open circuit mode at low losses. That is why the limits of application of DC motor with series excitation are not applied on ED of such type, also on ED, in mechanical parts of which are applied belt, tooth-belt and chain gears, since in such gears it is possible tearing and jumping of flexible elements from pulleys and stars, and consequently arrangement of conditions of open circuit at low losses, that can result to racing (fault of the motor because of high speed). At real conditions mechanical overrunning of commutating machine is not occur, because it will be preceded by electric damage – short circuit at machine input (racing).
From the shown on previous figure curves it should distinguish:
Natural characteristic. (is characterized at absence of additional resistance in armature circuit).
Limiting characteristic (is natural characteristic of idealized motor with real magnetic system, but internal resistance of armature circuit is absent. i. e. 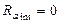 ;
; 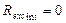 ). Since limiting characteristic is not depending on resistance of armature circuit, so it is multipurpose for definite type of electric motors.
). Since limiting characteristic is not depending on resistance of armature circuit, so it is multipurpose for definite type of electric motors.
Rheostat characteristics, which were described above.
It should recognize about of DC motor with series excitation. As for other DC motors, there are such reverse conditions: change of the sign of motor moment  into the opposite one by two methods:
into the opposite one by two methods:
The 1st method.  ;
;
The 2nd method. 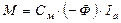 .
.
As opposed to DC motor with independent excitation, in DC motor with series excitation in physical essence armature winding and excitation winding are alike (almost the same cross – section of leads and current). Current reverse in excitation winding is unreasonable, because it should avoid machine magnetization foe safety of residual magnetization (one of required conditions of self excitation of DC machine with self excitation). So, reverse of the current for changing of rotation direction of the motor it is necessary to realize in armature winding, for example, by the help of the next scheme:
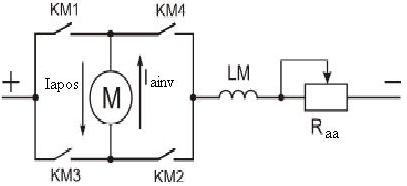
Motor reverse:
KM1, KM2 – are closed; KM3, KM4 – are opened (current Iapos flows through the armature, for example, for positive direction of rotation of DC motor with series excitation).
KM1, KM2 – are opened; KM3, KM4 – are closed (current Iainv flows through the armature for inverse direction of rotation).
Functional possibilities of DC motor with series excitation in braking modes are more limited comparatively with DC motor with independent excitation. So, braking mode with giving up the energy into the main (recuperative brake) is impossible at all because of the next reasons.
Emf of DC motor with series excitation can`t be more than applied supply voltage. Moreover, in even can`t be equal to supply voltage. If such condition will exist, the motor would have finite value ω0 (the speed of ideal open circuit). At approaching to such state motor speed increases sharp, thus making the possibility of emergency.
In addition, armature current changes its direction at passing of electric motor into the recuperative braking mode, but for DC motor with series excitation this current is also excitation current, i. e. also the direction of magnetic flux will reverse. Therefore, if realization of recuperative brake of DC motor with series excitation would be possible, the additional device for reversing of excitation current direction would be required.
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 1391; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!