
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Mechanical static characteristics of the motor in multimotor drive
|
|
|
|
SM mechanical static characteristics in braking modes
SM electrical braking can be realized only in two ways:
- counter switching;
- dynamic braking.
Counter switching braking is realized analogically to AM, rarely applied, since it is accompanied by significant current steps that exceed starting currents and significantly “fever” the main.
SM dynamic braking is more widely used (stator winding deenergized and closed on itself through the additional resistance).Braking intensity is higher that at counter switching, power losses is significantly less, impact blows and current steps are almost absent.
Braking intensity depends on value of resistance, on which the SM stator (armature) winding is closed.
There are cases when in ED system is not one but two or more engines on the total load.
Such systems have the next advantages comparatively with single motor drive:
- the more wide possibilities of speed and moment regulation;
- mutual machines reverse;
- decreasing total inertia moment of a system;
- designing of power plants with using of serial machines of comparatively small single power;
- simplification of mechanical equipment and better placement designing of electric motors;
- raising of reliability.
If there are two AM with phase rotor of half-power that is required by actuating mechanism, this will decrease the inertia moment almost in two-times, and if there is one motor of nominal power (inertia moment is proportional to the mass in the first power, and to linear size in the second power). Mechanical characteristics with small slopes can be obtained at this (both in motor and braking modes).
Since two rotors are mechanically rigid connected with each other, and stator windings are connected into a circuit in such a way that in motor mode the direction of motor moments coincides, so output system moment will be equal to algebraic sum of moments of single motors.
Figure 3.52 – Mixed mode (motor and braking) of double motor ED on a base of AM with phase rotor.
For obtaining of reduced speeds and mechanical characteristics with small slope it should to pass one of the machines into motor mode and the second – into mode of counter switching braking (look at the figure). Value of moments that every motor makes is provided by respective setting of active resistance in rotor circuit ( and
and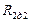 ).
).
If the motor AM1 operates in motor mode then M2 operates on mode of counter switching braking.
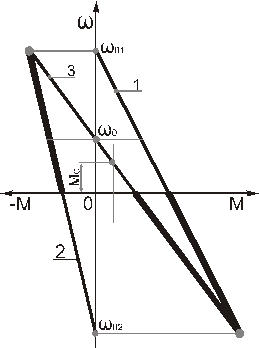
Figure 3.53 – Mechanical characteristic of double motor ED at mixed mode of motor operation.
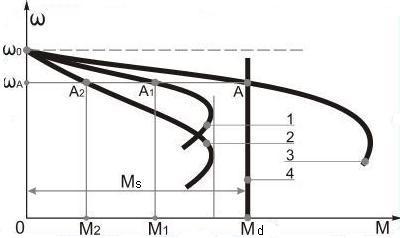
Mechanical characteristic of such drive is constructed as a moment sum of motor AM1 and motor AM2 for current speed values in motor and braking modes, on the figure:
1 – mechanical characteristic of motor AM1 (in motor mode);
2 – mechanical characteristic of motor AM2 (in counter switching mode);
3 – resulting mechanical characteristic of a drive.
As it seen from characteristic 3 the speed of ideal open-circuit 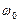 of ED is lower then synchronous speeds of the first and the second motors respectively
of ED is lower then synchronous speeds of the first and the second motors respectively and
and 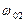 .
.
Mechanical characteristic slope of a drive (line 3) is less then a slope of 1st and 2nd motors characteristics, respectively 1line and 2.
Eventually the motive moment (or braking) of a drive (curve 3) equals to sum of the moments of both motors (curve 1 and 2)
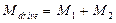 ,
,
where 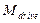 - drive moment;
- drive moment;
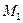 - the 1st motor moment;
- the 1st motor moment;
 - the 2nd motor moment.
- the 2nd motor moment.
Disadvantage of such scheme is significant heating of machine that operates in counter switching mode. To decrease the heating of a motor that operates in mode of counter switching braking it can be used in dynamic braking mode with independent excitation, not in mode of counter switching braking, and the 1st motor mode remains without changes.
The second example. If both motors (AM1 and AM2) operate in motor modes on the total load Ms let it be the motors with short-circuited rotor with different rigidity of mechanical characteristics (look at the scheme and figure on the next page).
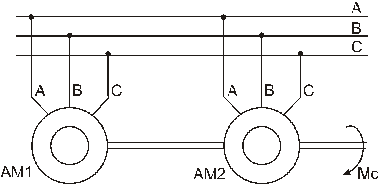
Figure 3.54 – Double motor ED for the case of both motor operations in motor mode.
There are:
1 – AM1 mechanical characteristic – of a motor with more rigid mechanical characteristic;
2 – AM2 mechanical characteristic – of a motor with less rigid mechanical characteristic;
3 – resulting mechanical characteristic of a drive;
4 – mechanical characteristic of actuating mechanism (load-lifting).
The 3 characteristic builds up as the total characteristic of the 1st and 2nd characteristics – mechanical characteristics of motors AM1 and AM2, stator windings of which are connected in such a way that both motors operate in the motor starting duty (both have the network connect: A, B, C) and motor shafts are rigidly bound between each other and connected with the load Ms (load-lifting mechanism).
Resultant moment Mres (3rd characteristic) equals Mres=M1+M2.
It is obviously that motors are loaded non-uniformly; motor with higher characteristic rigidity (AM1) is more loaded than motor with more flexible mechanical characteristic. So if both motors are with the same power then when the drive is completely loaded, motor AM1 will be overloaded and motor AM2 will be understressed. With the same rigidity if mechanical characteristics of motors they will be loaded uniformly.
That’s why when choosing the motors for operation under total load by mentioned above scheme the rigidity of mechanical characteristics should be considered.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 620; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!