
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Causes of the development of new meanings. Change of meaning
|
|
|
|
Polysemy. The semantic structure of polysemantic words
Lexical meaning and the semantic structure of English words
LECTURE 3
3.1. Lexical meaning and the semantic structure of English words. Generally speaking, meaning can be more or less described as a component of the word through which a concept is communicated, in this way endowing the word with the ability of denoting real objects, qualities, actions and abstract notions. The complex and somewhat mysterious relationships between referent (object, etc. denoted by the word), concept and word are traditionally represented by the following triangle:
Thought or Reference
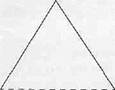
|
Symbol Referent
By the "symbol" here is meant the word; thought or reference is concept. The dotted line suggests that there is no immediate relation between word and referent: it is established only through the concept.
On the other hand, there is a hypothesis that concepts can only find their realization through words. It seems that thought is dormant till the word wakens it up. It is only when we hear a spoken word or read a printed word that the corresponding concept springs into mind.
The mechanism by which concepts (i. e. mental phenomena) are converted into words (i. e. linguistic phenomena) and the reverse process by which a heard or a printed word is converted into a kind of mental picture are not yet understood or described. Probably that is the reason why the process of communication through words, if one gives it some thought, seems nothing short of a miracle. Isn't it fantastic that the mere vibrations of a speaker's vocal chords should be taken up by a listener's brain and converted into vivid pictures? If magic does exist in the world, then it is truly the magic of human speech; only we are so used to this miracle that we do not realize its almost supernatural qualities.
The branch of linguistics which specializes in the study of meaning is called semantics. As with many terms, the term "semantics" is ambiguous for it can stand, as well, for the expressive aspect of language in general and for the meaning of one particular word in all its varied aspects and nuances (i.e. the semantics of a word = the meaning(s) of a word). As Mario Pei puts it in The Study of Language, "Semantics is 'language' in its broadest, most inclusive aspect. Sounds, words, grammatical forms, syntactical constructions are the tools of language. Semantics is language's avowed purpose."
The meanings of all the utterances of a speech community are said by another leading linguist to include the total experience of that community; arts, science, practical occupations, amusements, personal and family life.
The modern approach to semantics is based on the assumption that the inner form of the word (i. e. its meaning) presents a structure which is called the semantic structure of the word.
Yet, before going deeper into this problem, it is necessary to make a brief survey of another semantic phenomenon which is closely connected with it.
3.2. Polysemy. The semantic structure of polysemantic words. The semantic structure of the word does not present an indissoluble unity (that is, actually, why it is referred to as "structure"), nor does it necessarily stand for one concept. It is generally known that most words convey several concepts and thus possess the corresponding number of meanings. A word having several meanings is called polysemantic, and the ability of words to have more than one meaning is described by the term polysemy.
Two somewhat naive but frequently asked questions may arise in connection with polysemy:
1. Is polysemy an anomaly or a general rule in English vocabulary?
2. Is polysemy an advantage or a disadvantage so far as the process of communication is concerned?
Let us deal with both these questions together.
Polysemy is certainly not an anomaly. Most English words are polysemantic. It should be noted that the wealth of expressive resources of a language largely depends on the degree to which polysemy has developed in the language. Sometimes people who are not very well informed in linguistic matters claim that a language is lacking in words if the need arises for the same word to be applied to several different phenomena. In actual fact, it is exactly the opposite: if each word is found to be capable of conveying, let us say, at least two concepts instead of one, the expressive potential of the whole vocabulary increases twofold. Hence, a well-developed polysemy is not a drawback but a great advantage in a language.
On the other hand, it should be pointed out that the number of sound combinations that human speech organs can produce is limited. Therefore at a certain stage of language development the production of new words by morphological means becomes limited, and polysemy becomes increasingly important in providing the means for enriching the vocabulary. From this, it should be clear that the process of enriching the vocabulary does not consist merely in adding new words to it, but, also, in the constant development of polysemy.
The system of meanings of any polysemantic word develops gradually, mostly over the centuries, as more and more new meanings are either added to old ones, or oust some of them. So the complicated processes of polysemy development involve both the appearance of new meanings and the loss of old ones. Yet, the general tendency with English vocabulary at the modern stage of its history is to increase the total number of its meanings and in this way to provide for a quantitative and qualitative growth of the language's expressive resources.
When analyzing the semantic structure of a polysemantic word, it is necessary to distinguish between two levels of analysis.On the first level, the semantic structure of a word is treated as a system of meanings.
Yet, it is not in every polysemantic word that such a centre can be found. Some semantic structures are arranged on a different principle. In the following list of meanings of the adjective dull one can hardly hope to find a generalized meaning covering and holding together the rest of the semantic structure.
Dull, adj.
I. Uninteresting, monotonous, boring; e. g. a dull book, a dull film.
II. Slow in understanding, stupid; e. g. a dull student.
III. Not clear or bright; e. g. dull weather, a dull day,
a dull colour.
IV. Not loud or distinct; e. g. a dull sound.
V. Not sharp; e. g. a dull knife.
VI. Not active; e. g. Trade is dull. VII. Seeing badly; e. g. dull eyes (arch.). VIII. Hearing badly; e. g. dull ears (arch.).
Yet, one distinctly feels that there is something that all these seemingly miscellaneous meanings have in common, and that is the implication of deficiency, be it of colour (m. Ill), wits (m. II), interest (m. I), sharpness (m. V), etc. The implication of insufficient quality, of something lacking, can be clearly distinguished in each separate meaning.
The transformed scheme of the semantic structure of dull clearly shows that the centre holding together the complex semantic structure of this word is not one of the meanings but a certain component that can be easily singled out within each separate meaning.
This brings us to the second level of analysis of the semantic structure of a word. The transformational operation with the meaning definitions of dull reveals something very significant: the semantic structure of the word is "divisible", as it were, not only at the level of different meanings but, also, at a deeper level.
Each separate meaning seems to be subject to structural analysis in which it may be represented as sets of semantic components. In terms of componential analysis, one of the modern methods of semantic research, the meaning of a word is defined as a set of elements of meaning which are not part of the vocabulary of the language itself, but rather theoretical elements, postulated in order to describe the semantic relations between the lexical elements of a given language.
The scheme of the semantic structure of dull shows that the semantic structure of a word is not a mere system of meanings, for each separate meaning is subject to further subdivision and possesses an inner structure of its own.
Therefore, the semantic structure of a word should be investigated at both these levels: a) of different meanings, b) of semantic components within each separate meaning. For a monosemantic word (i. e. a word with one meaning) the first level is naturally excluded.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-07; Просмотров: 1883; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!