
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition
|
|
|
|
If the firm in an imperfectly competitive market has profit maximization as an objective, they will produce the output where marginal cost is equal to the marginal revenue. Short run profit maximization is shown in Figure 2.

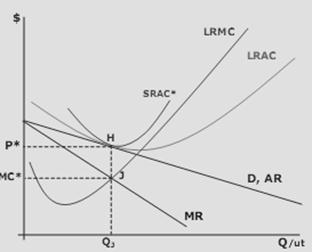
In the long run, above normal profits will attract the entry of firms into monopolistic competition. Below normal profits will encourage firms to exit. As firms enter the market demand is split among a larger number of firms which will shift the demand for each firm to the left (decrease) and probably make it more inelastic. There are more substitutes. Exit of firms will shift the demand for each firm’s output to the right (increase). Entry to and exit from the industry occur until the profits for each firm are normal, i.e. the AR = AC. The results of long run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market are shown in Figure 3.
The logical result of profit maximizing monopolistically competitive markets is to encourage firms to build plants that are smaller than optimal, i.e. a larger plant can produce with fewer inputs per unit of output (or costs per unit of output). Further inefficiency is expected since the inefficient plant is operated at an output level that is less than the minimum point on the SRAC. This result is due to the fact that the MR must be lower than AR when AR is negatively sloped.
Therefore MR=MC at less than the price which lies on the demand (or AR) function. Since the demand is negatively sloped and AC is usually U-shaped, the point of tangency between AR and LRAC (normal profits) will lie to the left of the minimum cost per unit of output. This is sometimes called the “ excess capacity theorem;” firms build plants that are too small and operate them at less than full capacity.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-11; Просмотров: 653; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!