
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
ES-моделирование для процессов с большим числом факторов, включающих также и качественные факторы
|
|
|
|
Раздел математики - комбинаторный анализ - представил ряд моделей и планов, позволяющих решать несложные задачи химической технологии с точки зрения поставленной цели, но с большим числом рассматриваемых факторов. Обычно этими методами решаются такие задачи:
задача исключения факторов источников неопределенности и их отсеивание;
задача разделения факторов на значимые и незначимые;
задача экспертной оценки.
В качестве планов эксперимента для модели
| yijql = m + ai + bj + cq + dl + eijql, | (1.3) |
где m - общее среднее, а остальные члены - это факторы на соответствующих уровнях плюс ошибка эксперимента 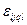 , используются Латинские квадраты, Греко - Латинские квадраты, Латинские кубы и др. Такого рода планы позволяют обойтись малым числом опытов и использовать Дисперсионный Анализ (ANOVA) для статистического анализа математической модели (см. пример в Табл. 1.2.).
, используются Латинские квадраты, Греко - Латинские квадраты, Латинские кубы и др. Такого рода планы позволяют обойтись малым числом опытов и использовать Дисперсионный Анализ (ANOVA) для статистического анализа математической модели (см. пример в Табл. 1.2.).
Табл.1.2. Результаты эксперимента по плану Греко-латинского квадрата.
| A B | b1 | b2 | b3 | b4 | b5 |
| a1 | c1 a 75.3 | c2 b 24.3 | c3 g 14.8 | c4 d 6.2 | c5 e 8.7 |
| a2 | c2 g 24.3 | c3 d 9.1 | c4 e 12.3 | c5 a 23.6 | c1 b 30.2 |
| a3 | c3 e 23.8 | c4 a 33.5 | c5 b 9.1 | c1 g 29.6 | c2 b 30.9 |
| a4 | c4 b 6.0 | c5 g 17.2 | c1 d 19.8 | c2 e 12.3 | c3 a 15.5 |
| a5 | c5 d 17.5 | c1 e 21.4 | c2 a 35.8 | c3 b 18.4 | c4 g 9.1 |
In this direction of ES-modelling, we would like to answer for the question: how to construct the optimal design in the condition of great number of factors when some of them are the qualitative and how to treat the results obtained? In the combinatorial analysis as a part of discrete mathematics, some methods were developed which are widely used in the multifactorial experimental design. For ones part, the requirements of the theory of planning design promote to create the new combinatorial methods.
Usually, in the engineer’s practice, three types of tasks are solved with the aid of combinatorial design application as follows:
· elimination task (when the experimenter wish to remove the source of heterogeneity);
· factor’s screening task (when the experimenter want to select the significant factors and throw aside insignificant ones);
· expert examination task (when a lot of treatment combinations should be considered and the planning of minimum treatments is very important).
Taking into consideration that the development of multicomponent composites involves the seeking of optimal composition, it is useful the factors (components levels) to be interpreted as a set of discrete elements. In this case, the techniques of combinatorial analysis suit to design the experiment by some optimal way. Here, the important task of combinatorial analysis is to decrease the number of design’s runs.
The most used multifactorial designs are the Latin Square, Creeko-Latin Square, Latin Cube etc. Notice, they are assumed that the effects of factors interaction are to be nonsignificant. The mentioned restriction allows to formulate the model of studied “quality-property” objects. So, for the Latin Cube design without replicate runs, the model of process is following:
yijql = m + ai + bj + cq + dl + eijql, (9)
where m is a common mean, ai is a factor A effect on the i- th level, bi is a factor B effect on the j -th level, cq is a factor C effect related to the first Latin letter on the q -th level, dl is a effect D related to the second Latin letter, eijql is a random error of experiment (see the next example).
Example of Creeko-Latin Square design 5*5 application for the optimal composition with oilgel and antipirine development. For the liquid form of drug with antipirine, it was decided to find the optimal composition which depends on kind of oil A (a1 - sunflower-seed, a2 - stone fruits, a3 - castor, a4 - vaseline, a5 - corn), type of detergent B (b1 - emulgator 1, b2 - emulgator 2, b3 - twin 80, b4 - voglan, b5 - pental), the percentage of aerosil C (c1 - 1%, c2 - 2%, c3 - 3%, c4 - 4%, c5 - 5%), and concentration of detergent D (a - 0.1%, b - 0.5%, g - 1.0%, d - 1.5%, e - 2.0%). Index: Aggregate stability of oilgel which makes packing available for gelatine capsules.
The treatment of results obtained (Table 1) was realised by the procedure ANOVA (analysis of variance). It is well known that ANOVA uses the calculating procedure developed still by Fisher. However, there are the new methods for the analysis of designed and observed matrices, in particular Marcova’s method where the analysis of variance is presented in the frame of regression analysis, that is with the least square method application. Thus, the successful attempt
was made to spread the famous treatment approach for continuous factor’s data onto discrete and qualitative factors [7].
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-13; Просмотров: 2292; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!