
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Low aspect ratio wings
|
|
|
|
High-aspect-ratio wings
Wing lift coefficient
In general case 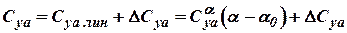 .
.
At small angles of attack  and
and  the lift coefficient of a wing is determined by equality
the lift coefficient of a wing is determined by equality
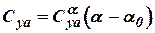 . (5.5)
. (5.5)
In compliance with the linear theory the lift coefficient  in compressed gas is determined by the formula
in compressed gas is determined by the formula 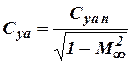 , where
, where 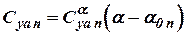 - lift coefficient of the deformed wing in incompressible gas. It follows from the last ratios, that
- lift coefficient of the deformed wing in incompressible gas. It follows from the last ratios, that
 ,
, 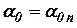 . (5.6)
. (5.6)
For incompressible fluid we have 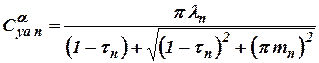 , where
, where 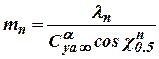 , (refer to section 4.1.1). As
, (refer to section 4.1.1). As 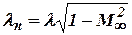 and
and 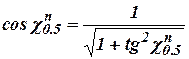 , then
, then  . Now
. Now 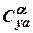 should be determined as
should be determined as  , where
, where  .
.
If assumes that  and
and  , then we get a result of a thin airfoil theory
, then we get a result of a thin airfoil theory 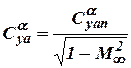 , where
, where 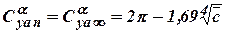 .
.
Parameter 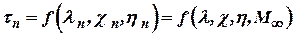 .
.
Approximately 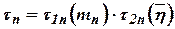 , where
, where 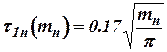 and
and 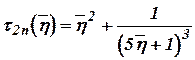 .
.
As non-linear lift component is absent for a wing of high aspect ratio 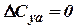 , then
, then  .
.
It is possible to use the formula for determination of a derivative of a lift coefficient by angle of attack 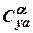 :
:
 , (5.7)
, (5.7)
where 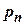 - parameter determined for a transformed wing.
- parameter determined for a transformed wing.
Particularly, we have for a tapered wing:

 .
.
Finally we shall write down the expression 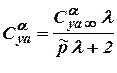 ,
,
where 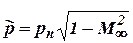 ,
,
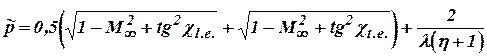 .
.
The non-linear additive is calculated under the formula:
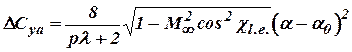 . (5.8)
. (5.8)
It is necessary to note, that the conversion linear theory can not be used for connection between compressed and incompressible flows while calculation of the non-linear additive  .
.
Thus:  .
.
5.1.3. Extreme small-aspect-ratio wings( ).
).
In such case we have  and
and 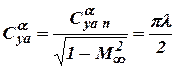 , therefore derivative
, therefore derivative  does not depend on Mach numbers
does not depend on Mach numbers 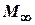 .
.
The non-linear additive  is determined by above mentioned formula (5.8).
is determined by above mentioned formula (5.8).
Note: it is possible to notice in the above mentioned formulae for 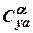 , that the ratio
, that the ratio  is a function of parameters
is a function of parameters 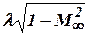 ,
,  and
and 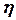 .
.
Parameter 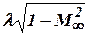 - reduced aspect ratio.
- reduced aspect ratio.
These parameters can be considered as parameters of similarity and used for creation of the diagrams. So 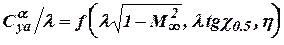 .
.
The analysis of wing lift in a subsonic gas flow:
1. The angle of zero lift  does not depend on numbers
does not depend on numbers 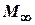 (Fig. 5.2).
(Fig. 5.2).
2. The derivative 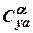 grows with increasing of numbers
grows with increasing of numbers 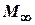 (Fig. 5.2).
(Fig. 5.2).
3. The effect of a compressibility (influence of Mach numbers 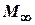 onto the derivative
onto the derivative 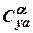 ) decreases with reduction of
) decreases with reduction of 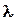 (it is the reason of spatial flow of low aspect ratio wings) (Fig. 5.3).
(it is the reason of spatial flow of low aspect ratio wings) (Fig. 5.3).
4. The non-linear component 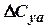 decreases with increasing of numbers
decreases with increasing of numbers 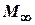 .
.

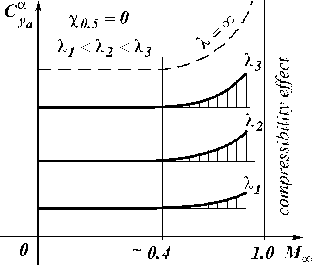
Fig. 5.2. Influence of number 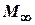 onto dependence onto dependence 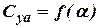
| Fig. 5.3. Influence of wing aspect ratio 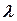 onto compressibility effect onto compressibility effect
|
5. The effect of a compressibility decreases with increasing of sweep angle 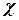 (Fig. 5.4). The reason of it - with rising up of sweep angle
(Fig. 5.4). The reason of it - with rising up of sweep angle 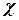 , the speeds component normal to the leading edge from which depends the characteristic
, the speeds component normal to the leading edge from which depends the characteristic  becomes less,.
becomes less,.
6. The value of 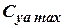 decreases with increasing of numbers
decreases with increasing of numbers 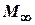 (reason - more earlier flow stalling) (Fig. 5.5). For example, for the airplane
(reason - more earlier flow stalling) (Fig. 5.5). For example, for the airplane  : at
: at 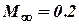 -
-  , and at
, and at  -
-  .
.
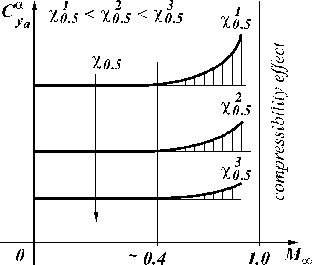

Fig. 5.4. Influence of a sweep angle 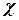 onto effect of compressibility at onto effect of compressibility at 
| Fig. 5.5. Influence of number 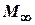 onto dependence onto dependence 
|
Using parameters of similarity the dependence 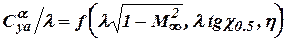 looks like it is shown in fig. 5.6.
looks like it is shown in fig. 5.6.
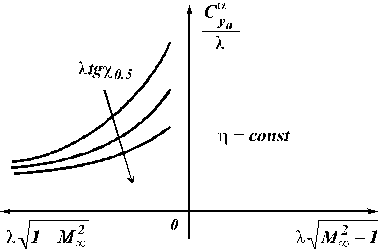
Fig. 5.6. Dependence of a factor  on parameters of similarity
on parameters of similarity
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-16; Просмотров: 412; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!