
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Induced drag
|
|
|
|
The wing induced drag coefficient taking into account of compressibility is equal
 , (5.9)
, (5.9)
Where 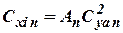 - induced drag of the “deformed” wing in incompressible gas flow;
- induced drag of the “deformed” wing in incompressible gas flow; 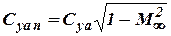 ; the polar pull-off factor is equal to:
; the polar pull-off factor is equal to:
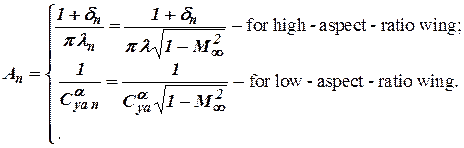
After substitution 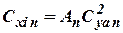 ,
, 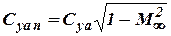 and
and  into (5.9) we again receive
into (5.9) we again receive
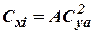 , (5.10)
, (5.10)
where  - for high-aspect-ratio wings,
- for high-aspect-ratio wings, 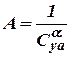 - for low-aspect-ratio wings.
- for low-aspect-ratio wings.
Thus formula of induced drag in gas subsonic flow is kept in a prior form (at angles of attack, where the linear dependence 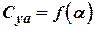 . Polar does not vary too (at condition of
. Polar does not vary too (at condition of 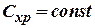 ).
).
5.3. Moment characteristics.
Location of center of pressure and aerodynamic center.
The factor of wing aerodynamic moment of pitch relatively to axis 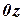 passing through center of forces reductions is determined by the formula
passing through center of forces reductions is determined by the formula
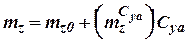 , (5.11)
, (5.11)
at that factor of pitch moment for linear part of dependence is determined as
Where 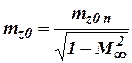 - factor of pitch aerodynamic moment at
- factor of pitch aerodynamic moment at 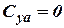 ,
, 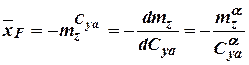 - relative coordinate of aerodynamic center position.
- relative coordinate of aerodynamic center position.
The position of aerodynamic center 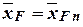 and center of pressure
and center of pressure  does not depend on Mach numbers
does not depend on Mach numbers  for a wing in subsonic and incompressible gas flows!
for a wing in subsonic and incompressible gas flows!
Received result is approximate for low-aspect-ratio wings with taking into account the non-linear effects. (it is exact at  ). For tapered high-aspect-ratio wings it is possible to offer the following formula for definition of aerodynamic center location relatively to wing top:
). For tapered high-aspect-ratio wings it is possible to offer the following formula for definition of aerodynamic center location relatively to wing top:
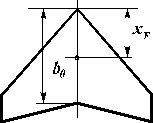 Fig. 5.7.
Fig. 5.7.
|
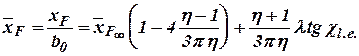
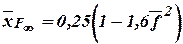 - airfoil.
- airfoil.
It is noteworthy, that if concepts of  and
and 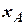 are used, then position of aerodynamic center relatively to the leading edge MAC in shares of
are used, then position of aerodynamic center relatively to the leading edge MAC in shares of  for wings of large aspect ratio is determined by the formula:
for wings of large aspect ratio is determined by the formula:
 Fig. 5.8.
Fig. 5.8.
|
 ;
;
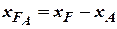 .
.
It is possible to consider this ratio as fair for wings with curvilinear edges or with fracture (Fig. 5.8). At that position of aerodynamic center relatively to wing top is determined by the formula:
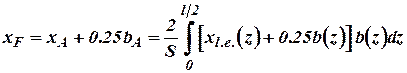 .
.
There is no the common formula for low-aspect-ratio wings. In particular cases: 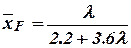 - rectangular wing,
- rectangular wing, 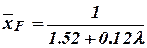 - triangular wing.
- triangular wing.
It is noteworthy, that the aerodynamic center displaces forward with decreasing of 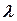 for rectangular wing (at
for rectangular wing (at 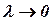 ,
,  and all aerodynamic load is concentrated on the leading edge), and the aerodynamic center with
and all aerodynamic load is concentrated on the leading edge), and the aerodynamic center with 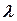 reduction displaces back for triangular wing (at
reduction displaces back for triangular wing (at 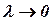 ,
, 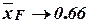 , more precisely
, more precisely  ).
).
5.4. Wing critical Mach number 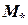 .
.
 Fig. 5.9. Christianovich dependence
Fig. 5.9. Christianovich dependence
|
The critical Mach number 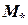 determines the upper border of subsonic flows and the above mentioned formulae are fair at condition of
determines the upper border of subsonic flows and the above mentioned formulae are fair at condition of 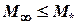 . Generally
. Generally 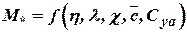 . Parameters
. Parameters  ,
,  and
and  have the greatest influence. The value
have the greatest influence. The value  can be defined by theoretical curve by
can be defined by theoretical curve by
S.A. Christianovich (Fig. 5.9), having the diagram of distribution of pressure factors  along wing surface in incompressible flow. It is also possible to use the following formula for assessment
along wing surface in incompressible flow. It is also possible to use the following formula for assessment 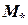 of wings with ordinary airfoils (Fig. 5.10) at lift coefficient value
of wings with ordinary airfoils (Fig. 5.10) at lift coefficient value  :
:
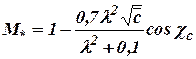 , (5.12)
, (5.12)
Where 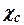 - sweep angle at a line of maximum thickness.
- sweep angle at a line of maximum thickness.
Other formula
 ;
; 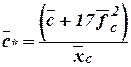 , (5.13)
, (5.13)
Where 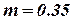 - classical airfoil,
- classical airfoil,  - supercritical airfoil.
- supercritical airfoil.
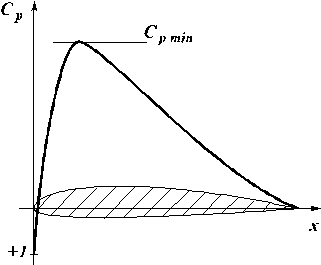
As it is visible from the above mentioned formulae, the value of 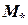 depends on relative thickness
depends on relative thickness  and airfoil camber
and airfoil camber  , on the airfoil shape (first of all on maximum thickness location
, on the airfoil shape (first of all on maximum thickness location 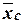 ) and on the wing plan form
) and on the wing plan form 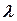 ,
, 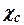 .
.
It is possible to increase 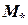 by application of supercritical airfoils (Fig. 5.11). They are characterized by more uniform distribution of a pressure factor chord lengthwise.
by application of supercritical airfoils (Fig. 5.11). They are characterized by more uniform distribution of a pressure factor chord lengthwise.

| Fig. 5.10. Pressure distribution on the upper surface for ordinary airfoil | Fig. 5.11. Pressure distribution on the upper surface for supercritical airfoil |
The account of 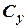 influence can be done by the following formula
influence can be done by the following formula
 . (5.14)
. (5.14)
It is possible to use dependence for supercritical airfoil and wings with such airfoils:
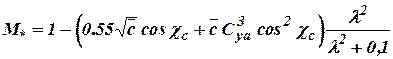 . (5.15)
. (5.15)
At  the last formula gives for supercritical airfoils
the last formula gives for supercritical airfoils 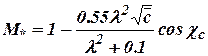 .
.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-16; Просмотров: 429; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!