
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Networks and their main purposes. PAN. LAN. A home area network. A campus network. Man. WAN. Gan. VPN. Internetwork. Overlay networks
|
|
|
|
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of computers and devices connected by communications channels that facilitates communications among users and allows users to share resources and peripherals with other users. The main purposes of the networks are:
A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for communication among computer and different information technological devices close to one person. Some examples of devices that are used in a PAN are personal computers, printers, fax machines, telephones, PDAs, scanners, and even video game consoles.
Local area networks (LANs) are usually placed in the same building. They can be built with two main types of architecture: peer-to-peer, where the twocomputers have the same capabilities, or client-server, where one computer acts as the server containing the main hard disk and controlling the other workstations or nodes, all the devices linked in the network (e.g. printers, computers, etc.).
Computers in a LAN need to use the same protocol, or standard of communication. Ethernet is one of the most common protocols for LANs. A router, a device that forwards data packets, is needed to link a LAN to another network, e.g. to the Net.
A home area network is a residential LAN which is used for communication between digital devices typically deployed in the home, usually a small number of personal computers and accessories, such as printers and mobile computing devices. An important function is the sharing of Internet access, often a broadband service through a CATV or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) provider.
A campus network is a computer network made up of an interconnection of local area networks (LANs) within a limited geographical area. The networking equipments (switches, routers) and trasmission media (optical fiber, copper plant) are almost entirely owned (by the campus tenant / owner: an enterprise, university, government etc.).
In the case of a university campus-based campus network, the network is likely to link a variety of campus buildings including; academic departments, the university library and student residence halls.
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that connects two or more local area networks or campus area networks together but does not extend beyond the boundaries of the immediate town/city. Routers, switches and hubs are connected to create a metropolitan area network.
A wide area network (WAN) is a computer network that covers a large geographic area such as a city, country, or spans even intercontinental distances, using a communications channel that combines many types of media. They are usually linked through telephone lines, fibre-optic cables or satellites. The main transmission paths within a WAN are high-speed lines called backbones.
Wireless WANs use mobile telephone networks. The largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
A global area network (GAN) is a network used for supporting mobile communications across an arbitrary number of wireless LANs, satellite coverage areas, etc. The key challenge in mobile communications is handing off the user communications from one local coverage area to the next. Wi-Fi, wireless fidelity, technologies allow the creation of WLAN s, where cables or wires are replaced by radio waves. To build a WLAN you need access points, radio-based receiver-transmitters that are connected to the wired LAN, and wireless adapters installed in your computer to link it to the network. Hotspots are WLANs available for public use in places like airports and hotels, but sometimes the service is also available outdoors (e.g. universitycampuses, squares, etc.).
A virtual private network (VPN) is a computer network in which some of the links between nodes are carried by open connections or virtual circuits in some larger network (e.g., the Internet) instead of by physical wires. The data link layer protocols of the virtual network are said to be tunneled through the larger network when this is the case. One common application is secure communications through the public Internet, but a VPN need not have explicit security features, such as authentication or content encryption. VPNs, for example, can be used to separate the traffic of different user communities over an underlying network with strong security features.
An Internetwork is the connection of two or more private computer networks via a common switching or routing technology and owned by separate entities (public or private). The result is called an internetwork. The Internet is an aggregation of many Internetworks hence it's name was shortened to Internet.
Any interconnection between public, private, commercial, industrial, or governmental networks may also be defined as an internetwork or (more often) an extranet.
The Internet is a global system of interconnected governmental, academic, corporate, public, and private computer networks. It is based on the networking technologies of the Internet Protocol Suite.
An overlay network is a computer network that is built on top of another network. Nodes in the overlay can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network. For example, many peer-to-peer networks are overlay networks because they run on top of the Internet. Internet was built as an overlay upon the telephone network.
30. Topology of networks: star, extended star, bus, ring, mesh networking, tree.
Topology of networks refers to the shape of a network. There are some basic physical topologies.
Star: there is a central device to which all the workstations are directly connected. This central position can be occupied by a server, or a hub. All traffic that transverses the network passes through the central hub. The hub acts as a signal booster or repeater. The star topology is considered the easiest topology to design and implement. An advantage of the star topology is the simplicity of adding additional nodes. The primary disadvantage of the star topology is that the hub represents a single point of failure.
Extended star: a type of network topology in which a network that is based upon the physical star topology has one or more repeaters between the central node (the 'hub' of the star) and the peripheral or 'spoke' nodes, the repeaters being used to extend the maximum transmission distance of the point-to-point links between the central node and the peripheral nodes beyond that which is supported by the transmitter power of the central node or beyond that which is supported by the standard upon which the physical layer of the physical star network is based.
Bus: every workstation is connected to a main cable called a bus. Each computer or server is connected to the single bus cable through some kind of connector. A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the IP address on the network that is the intended recipient. If the machine address does not match the intended address for the data, the machine ignores the data. Alternatively, if the data does match the machine address, the data is accepted. Since the bus topology consists of only one wire, it is rather inexpensive to implement when compared to other topologies.
Ring: the workstations are connected to one another in a closed loop configuration. Each machine or computer has a unique address that is used for identification purposes. The signal passes through each machine or computer. The primary disadvantage of ring topology is the failure of one machine will cause the entire network to fail.
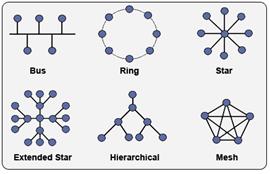
Mesh networking is a type of networking wherein each node in the network may act as an independent router, regardless of whether it is connected to another network or not. It allows for continuous connections and reconfiguration around broken or blocked paths by “hopping” from node to node until the destination is reached. A mesh network whose nodes are all connected to each other is a fully connected network. Mesh networks differ from other networks in that the component parts can all connect to each other via multiple hops, and they generally are not mobile.
Hierarchical network (also known as tree network): the type of network topology in which a central 'root' node (the top level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root' node, while each of the second level nodes that are connected to the top level central 'root' node will also have one or more other nodes that are one level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the third level) connected to it, also with a point-to-point link, the top level central 'root' node being the only node that has no other node above it in the hierarchy (The hierarchy of the tree is symmetrical.) Each node in the network having a specific fixed number, of nodes connected to it at the next lower level in the hierarchy, the number, being referred to as the 'branching factor' of the hierarchical tree.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2015-05-29; Просмотров: 1126; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!