
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Read the text and be able to answer some questions.
|
|
|
|
Wordbuilding
Wordbuilding
THE MOUTH CAVITY
-sub - префикс, указывающий на положение ниже чего-либо
lingual - язычный sublingual - подъязычный
1.Guess the meanings and translate:
group - группа subgroup -
division - деление subdivision -
maxillary - челюстной submaxillary -
mandibular - нижнечелюстной submandibular -
cutaneous - кожный subcutaneous -
conscious - сознание subconscious -
normal -нормальный subnormal -
structure - структура substructure -
title - заголовок subtitle -
2. Try to remember these word combinations before reading the text:
to be subjected to - подвергаться
the prime organs - главные органы
alveolar ridges - альвеолярные отростки
insalivation - смачивание слюной
deglutition - глотание
to be invested - быть погруженным
to pour saliva - изливать слюну
to extend - простираться
dentition - ряд зубов
3. Look at the picture and show the accessory organs of the digestive system:
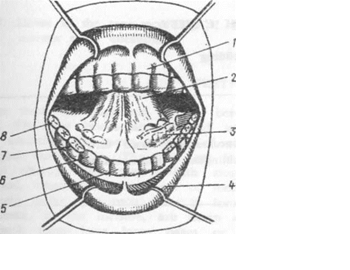 1 the gum
1 the gum
2 the tongue
3 the sublingual glands
4 the lips
5 the incisors
6 the canines
7 the premolars
8 the molars
9 the wisdom tooth
4. Read the text and be ready to answer some questions:
The mouth is an oval-shaped cavity situated at the beginning of the alimentary canal. In the mouth there are the teeth, tongue, and alveolar ridges, invested by the gum. The secretions of the parotid, submaxillary and sublingual glands are poured into the mouth cavity and in it the food is subjected to the processes of mastication and insalivation previous to deglutition. The teeth are the prime organs of mastication, and are implanted in the alveolar cavities.
A tooth is composed of four distinct structures:
1. The pulp occupying the chamber in the crown.
2. The dentine which constitutes the bulk of the organ.
3. The enamel which forms the protection of the crown.
4. The cementum which covers the root.
The teeth of the first dentition are termed deciduous or temporary teeth.
The temporary teeth are replaced by the permanent teeth. The anatomical divisions of a tooth are:
1. the crown or exposed part situated above the gum;
2. the root occupying the alveolar cavity of the socket;
3. the neck which is between the crown and the root.
The temporary teeth are twenty in number, ten in each jaw, namely: four incisors, two canines and four molars.
The permanent teeth are thirty two in number, sixteen to each jaw, namely: incisors - four, canines - two, premolars - four, molars - six. The third or last molar is called the wisdom tooth.
The incisors occupy the anterior central part of each maxillary arch. The function of this class of teeth is to cut the food.
The canine teeth are situated next to the incisors, two to each jaw. These teeth are for tearing the food.
The premolars, four to each jaw, are next to the canine teeth. They have two distinct cusps on their surfaces.
The molars occupy the posterior part of the alveolar arch and are six on each jaw. The function of the premolars and molars is to grind the food during mastication.
1. What sets of teeth do you know?
2. How many deciduous teeth are there on each jaw?
3. How many permanent teeth are there on each jaw?
4. Where is the mouth situated?
5. What classes of teeth are there?
EXERCISES
Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the fast reading of it.
Ex. 2. Give English equivalents:
овально-очерченная полость, секреция, жевание, ячейка, челюстная дуга, бугорок, разрезать пищу, первый ряд зубов, глотание, подвергаться, размалывать пищу.
1. The mouth cavity is situated... the beginning... the alimentary canal.
2. The tongue, teeth and the alveolar ridges are... the mouth cavity.
3. The teeth are the prime organs... mastication.
4. The enamel forms the covering and protection... the crown.
5. The incisor teeth are used... cutting the food.
6. The premolars have two distinct cusps... their grinding surfaces.
Ex. 3 Give the correct forms of the verbs.
1. The patient (to examine) by the doctor tomorrow.
2. The teeth (to implant) in the jaw bones.
3. The roots of the upper wisdom tooth (to unite) form one root.
4. We (to ask) by our professor to diagnose the case.
5. The food (to grind) during mastication by the teeth.
6. The secretion (to pour) by salivary glands.
Ex..4 Translate the text without a dictionary:
The mouth is a part of the digestive system. There are the teeth, tongue, and salivary glands in the mouth. The cavity of the mouth is divided into two portions: the vestibule and the cavity proper. The vestibule of the mouth is a space bounded by the lips and cheeks. The lips and cheeks contain the mimic muscles. The oral cavity proper is bounded by the hard and soft palates. The hard palate separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. The mucous membrane covers the lips, and cheeks to the alveolar processes of the jaws. In the mouth the food is ground by the teeth and mixed with water, mucous and other secretions of the salivary glands. Saliva has the direct influence on the teeth and provides an optimal level of metabolic activity in the body. There are many salivary glands in the mouth; three principal pairs are recognized: the sublingual glands, submaxillary glands and parotids. The salivary glands regulate the water supply of the body.
Ex. 5. Answer the questions and check your answers:
1. What organs are there in the mouth cavity?
2. What does the mucous membrane cover?
3. What place do the molars (canines, incisors) occupy in the mouth cavity?
Lesson 8
DENTAL TISSUES
-ive - суффикс, образующий прилагательные со значением "способный на ч/л"
to form - образовывать formative - образовательный
to talk - разговаривать talkative - разговорчивый
1. Choose the right Russian equivalent:
EXPRESSIVE 1. Выраженный
2. выражаемый
3. выразительный
DECISIVE 1. решенный
2. решительный
3. решающий
CONNECTIVE 1. соединительный
2. соединенный
3. соединяемый
DIRECTIVE 1. направляющий
2. направляемый
3. направленный
2. Translate the international words and the words of Latin and Greek origin:
a function, to protect, substance, the gingiva, a process, compact, the characteristic form, implanted, friction, tactile.
3. You'll come across these word combinations in the text:
dental tissues - зубные ткани
supporting tissues - поддерживающие ткани
exposed tissues - незащищенные ткани
to wear - носить, изнашивать(ся)
to resemble - напоминать
beyond the border - выше границы (над границей)
amount - количество
to overlap - перекрывать
to fasten - прикреплять
suspensory mechanism - поддерживающий механизм
to give rise to smth. - дать начало ч.-л.
The human teeth are made up of four tissues: the enamel, the dentine, the cementum and the pulp.
The enamel is the white, compact and very hard substance. The enamel covers the exposed parts of the softer underlying dentine. Its function is to protect the tooth against the wear and friction.
The dentine is the chief substance or tissue of the teeth composing the bulk of the tooth and the characteristic form of the tooth. It surrounds the tooth pulp, and is covered by the enamel on the exposed part of the tooth and by the cementum on the part implanted in the jaw. The dentine resembles a bone, but is harder and denser.
The cementum closely resembles in structure an ordinary bone. It covers the dentine beyond the border of the enamel, overlapping it slightly at the gingival line and forming the surface of the root. Its function is to furnish the attachment of the fibres of the periodontal membrane which fastens the tooth to the bone.
The cementum is relatively small in amount in the child but it increases during life.
The pulp is the soft vascular tissue occupying the pulp chamber and the root canals of a tooth, composed of nerves, blood vessels and connective tissue. It is the remain of the formative organ which has given rise to the dentine. The pulp of the tooth is one of the most sensitive structures of the body.
THE SUPPORTING TISSUES
The human teeth are supported on the alveolar and supporting bones,
the periodontal membrane and the gingivae. The alveolar processes of the
maxillary bones grow up around the roots of the teeth, so that the roots
fit into the holes of the bone. The periodontal membrane performs three
functions:
(a) it maintains the teeth in their functional positions through its
suspensory mechanisms;
(b) it takes part in the formation of the bone of its own alveolar walls and of the cementum;
(c) it provides through its tactile sensory mechanisms, for protection against the swallowing of hard, sharp and potentially dangerous materials.
1. What dental tissues do you know?
2. What is the enamel?
3. What is the chief tissue of the teeth?
4. Where does the cementum cover the dentine?
5. What is the most sensitive structure of the body?
6. Does the periodontal membrane support the teeth against the forces of mastication?
EXERCISES
Ex. 1. Listen to the tape-recording of the text and prepare the reading of it.
Ex. 2. Give English equivalents:
зубные ткани, поддерживающие ткани, защищать, изнашивать, трение, незащищенные ткани, по десневой линии, над границей, перекрывать, поддерживающий механизм, защита, альвеолярные отростки, осязательный, образовательный.
\
Ex. 3. Supply the correct form of the Participle:
1. The cases (to report) in the medical journals show that the inflammation of periosteum may be very serious.
2. To woman (to sit) at the patient's bed is a demist and she wants to examine his teeth.
3. (To have) severe toothache, the patient asks the doctor to give him some soothing medicine.
4. This patient (to place) under treatment early enough avoided the inflammation of periosteum.
5. (To suffer) from severe toothaches one must seek medical advice.
Ex. 4. Translate, using the necessary form of the Participle:
1. Дентин - это твердая зубная ткань, составляющая основу зуба.
2. Пульпа - это мягкая ткань, заполняющая центральную полость дентина.
3. Так как у вас стоматит, вы не должны курить.
4. Зубы человека, состоящие из 4-х тканей, располагаются на альвеолярных отростках челюстных костей.
Ex. 5. Answer the following questions and check your answers:
1. What are the human teeth made up of?
2. What does the enamel cover?
3. What is the function of the enamel?
4. What does the dentine compose?
5. What does the cementum cover?
6. What is the function of the cementum?
7. What is the pulp?
8. What are the human teeth supported on?
9. What are the functions of the periodonta) membrane?
Ex. 6. Translate the text without a dictionary.
The cement is the layer of a modified bone which encases the whole of the tooth except its crown. It begins at the neck as a very thin layer which slightly overlaps the enamel. From there it is continued increasing in amount towards the apex, which is formed entirely of this substance. It is relatively, small in amount in children, but it increases during life.
The pulp of the tooth is composed of a number of branched fibrous tissue ceils. Their processes form a fine network, which contains numerous blood-vessels, nerves, and lymph vessels. The most superficial of these cells are arranged in the young tooth, lying on the surface of the tooth against the destine; they are known as odontoblasts for they are active in the formation of the dentine.
The vessels of the tooth-pulp are numerous. Fine nerve bundles run through the pulp, the root canals towards the crown of the tooth and some of their fibres enter the odontoblasts Sayer. The alveolar periosteum is a layer of fibrous tissue free from elastic fibre but well supplied both with blood vessels and nerves.
Ex. 7. Answer these questions and check your answers:
1. What does the cement encase?
2. Where does the cement begin?
3. Is the cement small in amount in children?
4. What do the processes of the pulp form?
5. What are odontoblasts?
6. What is the alveolar periosteum?
7.
Ex. 8. Speak on the dental tissues and their functions using the picture below.
Lesson 9
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2017-02-01; Просмотров: 327; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!