
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Structural semantic
|
|
|
|
The Word.
A certain reflection in our mind of objects, phenomena or relations that makes part of the linguistic sign.
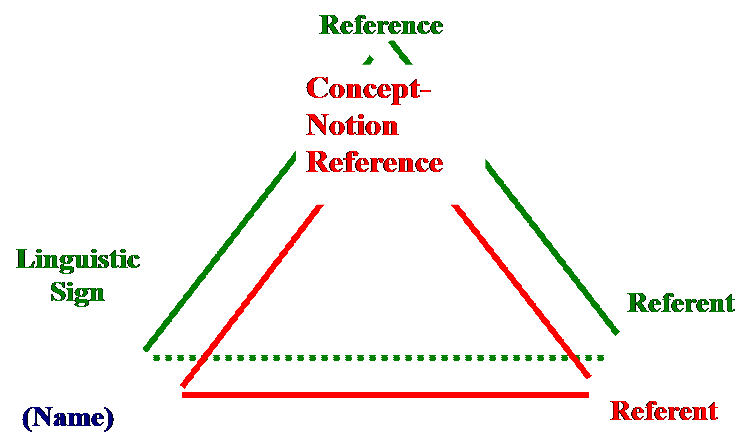
A sign is a two-facet unit comprising form (phonetic and orthographic), a linguistic symbol and reference which is more linguistic than a concept. A referent belongs to extra-linguistic reality, it is generalized in our minds as a concept and reflected in the meaning within the vocabulary.
Triangle of signification,
Semantic triangle,
Gotlieb Frege(1848-1925)
C.K. Ogden and I.A. Richards’ triangles:
Frege’s semiotic triangle,
O. and R.’s basic triangle
Referential approach:
 | |||
|
Word meaning –
ESSENTIAL WORD CHARACTERISTICS:
 |
| Phonetic Structure Morphological Structure Grammatical Structure Syntactic Structure | Nominal Onomastic character Significant Indivisible Isolated | ||||
Types of Word
Eight kinds of words
The orthographic word
The phonological word
The morphological word
The lexical word
The grammatical word
The onomastic word
The lexicographical word
The statistical word
Motivation is the relationship btw. the phonetic or morphemic composition and structural pattern of the word on the one hand and its meaning on the other.
Three main types of motivation (inner word form):
Phonetical: a certain similarity btw. the sounds and the sense:
(bang, buzz, giggle, gurgle, hiss, purr),Cuckoo.
Sound imitative words (eco-words):
Babble, chatter, gabble, prattle; purr, moo, crow, bark, bleat.
Morphological motivation or word-building meaning:
ex ‘former’:
(ex-president, ex-wife); but expect, export( borrowed wds – no motivation )
re-‘again, back’(rebuild, reclaim, resell) but recover “get better”
Word-building meaning: V +-er =N:
Writer,receiver,bomber,rocker,knocker but number(OFr nombre) and smoker(a fuzzy set).
Semantic motivation:
coexistence of direct and figurative meanings of the same words:
(mouth of a river, cave, furnace), (jacket of a book, electric fire.)
Morphological and semantic motivation in compound words (eyewash, headache, watchdog).
First-nighter, honeymooner, two- seater, three-decker (a sandwich) are different in their motivation: lick-spittle “a flattering or a servile person”.Teenager”a person in his or her teens ” (historically traced).
Non-motivated words:
No connection btw. meaning and its form at the present stage of lg. development:
earn > (ge) earnian “to harvest”;
not > nought > OE nowiht <no-wiht “nothing”.
Faded motivation:lost in the history and not felt at present.
Folk etymology or mistaken motivation (a nightmare, may-day”SOS”).
Sound symbolism:
fl – quick movement:
flap, flip, flop, flitter, flimmer, flicker, flutter, flash, flush, flare;
(but flat, floor, flower)
gl(light, fire) – glare, glitter, glow, glimmer;
sl(mud)-sleet,slime,slush but sleep, slender.
TEST
1. Name as many approaches to the word definition as possible.
2. Enumerate types of a word.
3. Give examples of different motivations of words.
Lecture 3
Lexical Meaning and Semantic structure of English Words
Outline
1. Semantics and Semasiology
2. The lexical meaning versus notion
3. Denotative and connotative meaning
4. The semantic structure of polysemantic words
5. Contextual analysis
6. Componential analysis
SEMANTICS
¨The meaning of words and phrases
¨Study of Linguistic meaning
¨Study of relationship between the sign and the referent
WEBSTER’S UNABRIDGED DICTIONARY
¨ The study of linguistic development
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2013-12-13; Просмотров: 843; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!