
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Conservative and nonconservative forces
|
|
|
|
Potential Energy and External Work
As we have just seen, work done by an external agent can change the potential energy of a system. We may use this fact to present an initial, tentative definition of potential energy. If the external force on an apple (say) exactly balances the gravitational force, the speed and kinetic energy of the apple does not change. In this case, all the external work must appear as a change in the potential energy U:
(υ constant) W EXT = +∆ U = U f − U i (4.13)
Positive external work leads to an increase in the potential energy of a system.
Equation 4.13 shows that only changes in potential energy are significant. This gives us the freedom to assign U = 0 to whatever configuration is convenient. (By configuration we mean the arrangement of the particles in a system, or equivalently, the shape of a deformable body.) When a particle moves near the surface of the earth, we set the zero of gravitational potential energy, Ug = 0, at any convenient horizontal level, such as the ground or a tabletop. In the case of a spring, it is customary to choose the zero of the spring's potential energy, Usp = 0, at x = 0, where there is neither expansion nor compression. If the initial configuration has zero potential energy, then WEXT = Uf − 0 = U f:
The potential energy of a system is the external work needed to bring the particles from the U = 0 configuration to the given positions at constant speed.
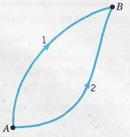
|
| FIGURE 4.6 |
The force of gravity and the force exerted by an ideal spring are called conservative forces, whereas the force of friction is a nonconservative force.
When a particle moves under the influence of a conservative force from A to B, as in Fig. 4.6, the work done on the particle by the conservative force is the same for path 1 and for path 2:
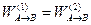 (4.14)
(4.14)
The work done by a conservative force is independent of the path taken.
If we reverse the direction of travel along path 2 in Fig. 4.6, the force is unchanged but each of the infinitesimal displacements is in the opposite direction. Therefore, the sign of the work will change: 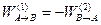 . Equation 4.14 may therefore be rewritten as
. Equation 4.14 may therefore be rewritten as
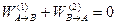 (4.15)
(4.15)
The work done by a conservative force around any closed path is zero.
In order for the work done by a conservative force not to depend on the path, the force must be a function only of position, not of velocity or time. The magnetic force on a moving charge and fluid resistance are velocity dependent, which means they are nonconservative. The force exerted by a hand can vary in time; hence, it is also nonconservative.
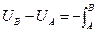 F c· d s (4.16)
F c· d s (4.16)
Potential energy can be defined only for a conservative force, because only the work done by such a force does not depend on the path taken. From Eq. 4.16 we see that starting with potential energy UA at point A, we obtain a unique value UB at point B, because Wc has the same value for all paths. When a block slides along a rough floor, the work done by the force of friction on the block depends on the length of the path taken from point A to point B. There is no unique value for the work done, so one cannot assign unique values for potential energy at each point.
Because friction is a common example of a nonconservative force, the term "nonconservative" is often taken to mean "dissipative," which implies that the force leads to a permanent loss in kinetic energy. This is incorrect. For example, the nonconservative magnetic force on a moving charged particle does not change the kinetic energy of the particle moving in a circular path. The nonconservative force exerted by a hand can either increase or decrease the kinetic energy of a particle in a round-trip journey. The distinction between conservative and non-conservative forces is best stated as follows:
A conservative force may be associated with a scalar potential energy function,whereas a nonconservative force cannot.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 438; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!