
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Springs
|
|
|
|
In Fig. 5.2 a, a block of mass m on a frictionless surface, is attached to a spring that is initially extended to x = A and then released. The force exerted by the spring will accelerate the block toward the equilibrium position x = 0. At an arbitrary point, the energy of the block-spring system is
E = 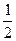 mυ2+
mυ2+
and the conservation of mechanical energy states
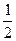 mυf2+
mυf2+ =
= 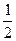 mυi2+
mυi2+

|
| FIGURE 5.2 |
At its initial point there is no kinetic energy and the system has its maximum potential energy: E = K + U = 0 + 1/2 kA 2. As the block speeds up and moves toward the origin, the gain in kinetic energy exactly balances the loss in potential energy so that their sum stays constant. At x = 0, the block has its maximum kinetic energy and zero potential energy, or E = K + U = 1/2 mυ 2max + 0. In summary,
E=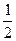 mυ2+
mυ2+ =
= 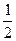 mυ 2max =
mυ 2max =  (5.6)
(5.6)
Assuming that the coils of the spring do not touch, the block continues its motion past x = 0. Its kinetic energy decreases as its potential energy increases, until finally at x = −A the energy is again purely potential: E = K + U = 0 + 1/2 kA 2. The variation of the kinetic and potential energies is shown in Fig. 5.2 b. Since the force due to the spring is always directed toward the origin, the block oscillates back and forth. The turning points are at x = ±A, where К = 0 and E = U max.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 382; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!