
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Grammar
|
|
|
|
TRANSISTORS IN COMPUTERS
Writing
Speaking
8. Explain how a field-effect transistor (FET) works. Use the diagrams in Fig. 3.5 and the information in the previous tasks to help you. Exercise the following words and word combinations:
· Field-Effect Transistor (FET);
· controlling the movement electrons;
· gate, source, drain;
· Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
· extra electrons in the n-type source and drain
· holes in the p-type gate
· a positive voltage, an electric field
· switch the transistor on and off
· a unipolar transistor
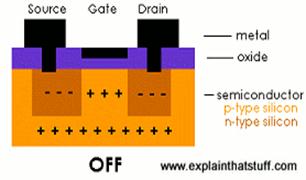
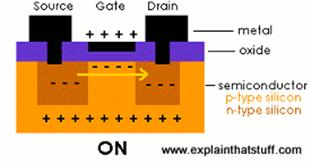
Fig.3.5. How a field-effect transistor (FET) works.
9. Work in pairs. Make dialogues about the difference between a bipolar and a field-effect transistor.
10. Make a comparative table of a bipolar and a field-effect transistor.
WHO INVENTED THE TRANSISTROR?
1. Study the sentences below and pay attention to the underlined verb forms in italics.
| Your brain contains around 100 billion cells called neurons. |
| Computers contain billions of miniature brain cells as well. |
| But what are they – and how do they work? |
| A transistor is really simple and really complex. |
| The small current switches on the larger one. |
| The most advanced transistors work by controlling the movements of individual electrons. |
Answer the following questions:
5) What are these verb forms?
6) is, are. What verb has such forms?
7) contains, switches. What do these verb forms have in common?
8) contain, work. Are these verb forms similar?
9) What tense are these verb forms in?
It is the Present Indefinite or Present Simple Tense.
2. How do we form sentences in the Present Indefinite? Complete the table.
| Positive | Negative | Interrogative |
| I, you, we, they + Verb. He, she, it +Verb + (e)s | Subject + do + not + Verb. Subject + does + not + Verb | Do+ Subject+Verb? Does + Subject + Verb? |
| I teach English every day. You He studies every day. She It We They | I do not teach every day. He does not study every day. | Do I teach every day? Does he study every day? |
3. So, now we can form the Present Indefinite. But when do we use the Present Indefinite? Study the following table and give your own examples.
| Actions happen… | Examples |
 Repeated actions, habits, routines:
every morning / evening / day / night
every week / month / year
usually
always
never
frequently/often
seldom/rarely
sometimes/occasionally/
from time to time
nowadays
Repeated actions, habits, routines:
every morning / evening / day / night
every week / month / year
usually
always
never
frequently/often
seldom/rarely
sometimes/occasionally/
from time to time
nowadays
| · We get up at 8 o’clock every morning. · Mary’s father reads newspapers every evening. · He usually goes home after work. · She always forgets her purse. · I never drink milk. · My friend often draws nice posters. · They rarely visit their parents. · Susan sometimes meets with her friends after school. · Nowadays all electronic devices use semiconductors. |
 Facts, generalizations, universal truths
Facts, generalizations, universal truths
| · Electrons have negative charges. · Silicon is a semiconductor. · Water boils at 100 degrees. · The Earth goes around the Sun. · Transistors work as amplifiers and switches. |
 Fixed arrangements, timetables
Fixed arrangements, timetables
| · The meeting starts at 4 p.m. · The train leaves at 10 a.m. · When does the plane take off? · The course starts in April. |
 With non-continuous verbs:
be, believe, belong, hate, hear, like, love, mean, prefer, remain, realize, see, seem, smell, think, understand, want, wish
With non-continuous verbs:
be, believe, belong, hate, hear, like, love, mean, prefer, remain, realize, see, seem, smell, think, understand, want, wish
| · I understand English. · You are students. · She believes in God. · He loves and hates her. · We know this rule. · They like everything about electronics. |
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-11-29; Просмотров: 521; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!