
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
ARP Protocol
|
|
|
|
The main application of the ARP protocol – is compliance establishment between the IP address of destination and the destination MAC address. When the computer addresses to other computer in an IP network (local or remote), for instructions of the addressee the destination IP address is used. However to transfer data on the Ethernet network, it is necessary to know the MAC address of the computer of destination if it is in a local network, or the MAC address of a gateway (router) through which it is necessary to transfer data if the addressee is located in other network. For MAC address definition to the IP address the ARP protocol (by Address Resolution Protocol, the protocol of permission of addresses) is used.
The ARP protocol works at a basis of Ethernet frames, i.e. the package of the ARP protocol is put in the data field of a Ethernet frame (thus value weeding type of the protocol of a Ethernet frame in a hexadecimal form – 0806). In figure 7.2.3 the ARP package format is presented.
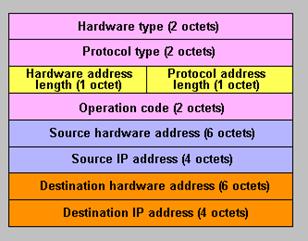
Figure 7.2.3 - ARP package Format (a destination field FCS of a Ethernet frame isn't shown)
The ARP package contains the following fields:
The address of destination and the address of a source are MAC addresses of the recipient and the frame sender. In the ARP message value of protocol type in a hexadecimal form (16) – 0806. This value identifies the ARP protocol which puts the package in the data field of Ethernet frame.
The first four fields of an ARP package serve for definition of two address structures between which compliance, and lengths of addresses used in them is established. The ARP protocol can be applied to different pairs related by it addresses of network and channel levels.
For Ethernet in the field the type of the hardware address is specified 1 that means use of the addresses Ethernet, i.e. MAC addresses, and a field length of the hardware address contains value 6, since length of the MAC address – 6 bytes. When using IP addresses in the field the type of the legal address is specified hexadecimal value 0800, i.e. the same value, as in the field type of the protocol of heading of Ethernet frame when in the data field of a Ethernet frame the IP package is enclosed. At this field the length of the legal address contains value 4, since length of the IP address – 4 bytes.
The field a code of operation determines ARP package type – request for MAC address definition by the known IP address or the answer with result of question. For ARP question in the field the code of operation is specified 1, and for the ARP answer – 2.
In the field the hardware address of the sender is specified the MAC address of the sender of this question or the answer, and this field contains the MAC address of the computer of destination requested in ARP request if it is in a local network, or the MAC address of a gateway (router) through which it is necessary to transfer data if the computer of destination is located in other network in the ARP answer.
In the field of the network address of the sender the IP address of the sender of this question or the answer is specified.
The field the hardware address of the recipient contains one zero that means in ARP questions that this information is unknown, and in ARP answers – the MAC address of the computer which has sent ARP question.
In the field of the network address of the recipient the IP address of the recipient of this question or the answer is specified.
When using the ARP protocol two situations are possible:
а) the recipient is in the same network, as the sender;
b) the recipient is in another in relation to the network sender.
However in any case the ARP protocol serves for clarification of the MAC address of only local node - the local recipient (computer) or a local router.
7.2.2.1 ARP protocol work when the sender and the recipient are located in one network. The computer A with the name Vito and the computer B with the name Maxx are in one network of the class C 192.168.0.0 which has not been divided into a subnets, and the computer A wants to transfer some data to the computer B. In figure 7.2.4 the arrangement of computers A and B with the indication of MAC addresses and IP addresses is shown.
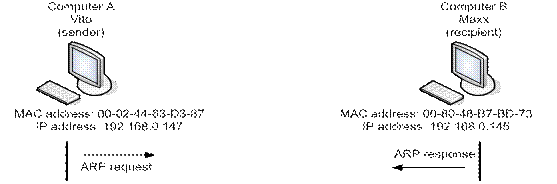
Figure 7.2.4 - Sender and recipient arrangement in one network
To transfer any data, the computer A should address to the computer B to its IP address 192.168.0.145 (on the computer A is entered the ping 192.168.0.145 team therefore on the computer B it will be sent an echo question). However on the physical channel data are transferred in Ethernet frame in which heading the computer MAC address, instead of the IP address should be specified. Compliances between IP addresses and MAC addresses of computers of one network are stored in the table of the ARP protocol located in special area of memory of each computer, and these compliances (records) can be static and dynamic. Static records are entered by the manager and stored before computer reset, and dynamic decide on the help of the ARP protocol and are stored for some time. By default this time is equal in the Windows operating systems to two minutes for unclaimed records and to ten minutes for records to which there was an address. For viewing of the table ARP of the computer the arp –a serves, and for removal of all records from the table ARP (table cleaning) the arp –d is used.
In Figure 7.2.5 it is given an example of arp –a, entered in a command line of the computer A. The computer A table ARP in this case contains one dynamic record reflecting compliance between the IP address and the MAC address of the computer B.
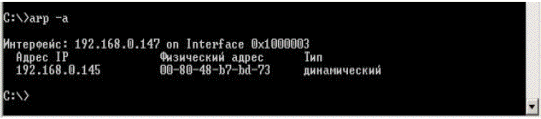
Figure 7.2.5 - The computer A Table ARP for a network presented in Figure 7.2.4
At the appeal to the computer B the computer A operates as follows. At first the computer A defines, in what network – local or remote – there is a computer B. For this purpose it carries out operation logic «And» for the IP address 192.168.0.147 and a standard mask of a subnet of a class C 255.255.255.0. Then it carries out operation logic «And» for the IP address of the B 192.168.0.145 computer and the same mask 255.255.255.0. If results of performance of these operations coincide (in this case results of both operations «And» – 192.168.0.0), the computer B is in the same network, as the computer A (i.e. in a local network) and if isn't present, the computer B is located in other (remote) network.
Then the computer A looks through own table ARP about existence in it of the record establishing compliance between the IP address and the MAC address of the computer B. If such record is available, the computer A enters the computer B MAC address in the field the address of purpose of heading of a Ethernet frame (see fig. 1) and transfers a frame to the computer B. If the necessary record isn't present, for clarification of the MAC address of the computer B the computer A uses the ARP protocol. For this purpose the computer A sends to a local network a broadcasting Ethernet frame (a frame without the destination MAC address) – Figure 7.2.6. The first four fields of an ARP package for simplicity are lowered, (at definition in the Ethernet network of MAC addresses to IP addresses contents of this field always same). In the field the address of destination there are all units, and in the field type of the protocol the protocol identifier equal 0806 (ARP protocol), in the field a code of operation is established the ARP package type (in this case it is ARP question therefore, value - 1), in the field of the network address of the recipient is defined – the computer B IP address is specified. At this field the hardware address of the recipient contains one zero that means that the MAC address of the computer B is unknown, and the computer A wants to find out this address. The broadcasting frame with ARP question is accepted by all computers of a network (in Fig. 7.2.4 only two computers are shown), but the answer to it should give only the computer which IP address coincides with the IP address specified in the field of the network address of the recipient, i.e. only the computer B.
The computer B, having processed the accepted frame, understands that some computer with the MAC address 00-02-44-63-D3-87 and the IP address 192.168.0.147 requests from it the MAC address. The computer B writes down in the table ARP compliance between the IP address and the MAC address of the computer A and sends to a local network Ethernet frame with the ARP answer (see Fig. 7.2.7), specifying in the field the address of purpose of heading of a frame the computer A MAC address. Thus, the frame with the ARP answer is sent not in broadcast, and is directed – to the computer which has sent ARP question. As we see in Figure 7.2.7, field the code of operation of an ARP package contains the value 2 identifying the ARP answer, and in the field the hardware address of the sender the computer B specifies the MAC address which requested the computer A.
Having received the ARP answer, the computer A writes down in the table ARP compliance between the IP address and the MAC address of the computer B and sends to the computer B a frame with data.

Figure 7.2.6 - Broadcasting transfer of ARP question by the computer A
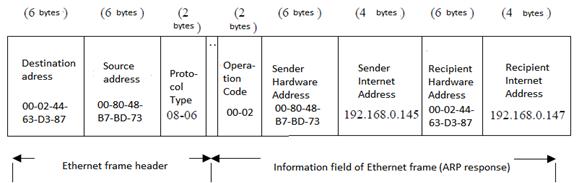
Figure 7.2.7 - The computer B ARP answer
7.2.2.2 ARP protocol work in a case when the sender and the recipient are located in different networks. Let the computer A with the name Vito and the computer B with the name Maxx as well as in the first case, are in one network of the class C 192.168.0.0 which has not been divided into a subnets, but the computer B is connected both to an external network and besides the usual functions carries out functions of a gateway (router). The computer A wants to address through an external network to some computer C with the IP address 195.5.27.10, i.e. the recipient is in other network. The corresponding illustration is given in Figure 7.2.8.

Figure 7.2.8 - Sender and recipient Arrangement in different networks
At the conversation of the computer A to the computer C, for example, at input – n 1 195.5.27.10, the computer A acts on the ping team computer A as follows.
At first the computer A defines, in what network – local or remote – there is a computer C. For this purpose it «overlap» a standard mask of a subnet of a class C 255.255.255.0 to the IP address 192.168.0.147 and receives result 192.168.0.0. Then it «overlaps» the same mask to the IP address of the computer recipient 195.5.27.10 and receives result 195.5.27.0. Since results of these two operations are various, the computer A draws a conclusion that the computer C is in other network and data transmission needs to be executed through a gateway (computer B).
Then the computer A should send Ethernet frame about an echo question, having specified in heading of the ICMP package enclosed in this frame the computer recipient 195.5.27.10 IP address, and in heading of a Ethernet frame – the gateway MAC address, i.e. the computer B (instead of the computer recipient MAC address) since at first the frame on the Ethernet network should reach a gateway. Therefore, the computer A should know the gateway MAC address, but in the TCP/IP settings of the computer the MAC address, and the gateway IP address is specified not. If the computer A addressed recently to a gateway, the MAC address of a gateway can be in the computer A table ARP. If the computer A after initial loading didn't address yet to a gateway or addressed to it long ago and the corresponding dynamic record of compliance “the IP address – the MAC address” is already removed, the table ARP of the computer A won't contain the gateway MAC address (if only it isn't entered there by the manager manually). In this case the computer A should find out the gateway MAC address by means of the ARP protocol.
Process of examination by the computer A of the MAC address of a gateway (computer B) is described above. After definition of the MAC address of a gateway the computer A sends an echo question to the computer C. This echo request arrives on the computer B which, carrying out router function, sends an echo request to the computer C through an external network.
At data transmission from the sender to the recipient being in a remote network, in heading of an IP package the IP address of the recipient is specified, and in heading of a Ethernet frame the MAC address not the recipient, and the gateway MAC address through which data should be transferred is specified. Similarly, at receipt the MAC address is pointed to the sender (computer A) of response data from the recipient (computer C) through a gateway (computer B) in the field of the MAC address of a source of heading of a Ethernet frame not the computer C, and the MAC address of a gateway (computer B), and in the field of the IP address of a source of heading of an IP package the IP address not a gateway In, and the computer C IP address is specified.
7.2.2.3 Use of ARP protocol for checking existence in network duplicated IP-adress. In addition to establishing the correspondence between MAC-addresses and IP-address, protocol ARP performs another important function. When you turn on (boot) the computer and changing its IP-address the ARP protocol allows you to determinewhether there is in the LAN computers with identical IP-addresses. For this when booting computer, and after changing its IP-address a computer sends aARP-request, where as the recipient of the package (field network address of the recipient) indicates its own IP-address.
Such an ARP-request is a self (from the word gratuitous – “causeless”, ie is not caused by the need to further data transmission or “gratuitous”, ie does not require an answer). The computer sends self ARP-request without waiting for an answer. If the answer to a self-ARP-request is not received, then the same IP-addresses ingiven computer in the network no longer exists. If any LAN computer is responding to a self-ARP-request by its MAC-address therefore in LAN already exists a computer with such IP-address. In this case, on the screen of computer that sent a self-ARP-request, and on the computer screen, responding to this request, displayed the error message – “The conflict of IP-address with another system in the network”.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 545; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!