
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Key information Section 1. An operating system (OS or o/s) is an interface
|
|
|
|

| 
| 
|
An operating system (OS or O/S) is an interface (connection) between hardware and user - it determines how the user interacts with the computer; it is responsible for the management and coordination of activities and the sharing of the resources of the computer. The operating system acts as a host for applications that are run on the machine, handling the details of the operation of the hardware. This relieves application programs from having to manage these details and makes it easier to write applications. The purpose of an operating system is to organize and control hardware and software so that the device it lives in behaves in a flexible but predictable way. The operating system is started automatically when a computer is switched on, it is the first thing loaded onto the computer - without the operating system, a computer is useless. It is then used to start up and control other programs.
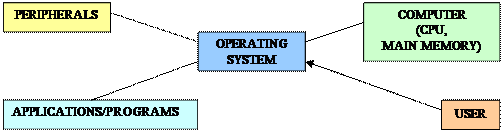
Common contemporary operating systems include Microsoft Windows (designed by Microsoft and used on most PCs), Mac OS (created by Apple and used on Macintosh computers). Microsoft Windows has a significant majority of market share in the desktop and notebook computer markets, while servers generally run on Unix or Unix-like systems (found on mainframes and workstations in corporate installations, as it supports multi-users). From the very first, it was designed to be a multi-tasking system. Written in C language, Unix is the most commonly used system for advanced CAD programs. Linux is a generic term referring to Unix-like multi-tasking computer operating systems based on the Linux kernel. Their development is one of the most prominent examples of free and open source software collaboration; typically all the underlying source code can be used, freely modified, and redistributed by anyone under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GPL) and other free licenses. Linux is predominantly known for its use in servers, although it is installed on a wide variety of computer hardware, ranging from embedded devices and mobile phones to supercomputers.
System software helps to run the computer hardware and computer system. It includes operating systems, device drivers, diagnostic tools, servers, windowing systems, utilities, language translator, data communication programs, data management programs and more. The purpose of systems software is to insulate the applications programmer as much as possible from the details of the particular computer complex being used, especially memory and other hardware features, and such accessory devices as communications, printers, readers, displays, keyboards, etc.
| Application software is any tool that functions and is operated by means of a computer, with the purpose of supporting or improving the software user's work. In other words, it is the subclass of computer software that employs the capabilities of a computer directly and thoroughly to a task that the user wishes to perform. This should be contrasted with system software (infrastructure) or middleware (computer services/ processes integrators), which is involved in integrating a computer's various capabilities, but typically does not directly apply them in the | 
| ||

| performance of tasks that benefit the user. In this context the term application refers to both the application software and its implementation. Utility software (also known as service program, service routine, tool, utility routine or system utilities) is computer software designed to help manage and tune the computer hardware, operating system or application software by | ||
performing a single task or a small range of tasks which improve a system's performance and help users take advantage of the computer's capabilities. Utility software has long been integrated into most major operating systems. Utilities are often desk accessories that can be called up while you're working in another application. They can also be system extensions which are activated when you turn on the computer, control devices which you adjust in the control panel, or even stand-alone programs that run when you need them.
Utilities are available for back-up, file search, virus protection, disaster recovery, and so on.
Accessibility program makes a PC easier for disabled users to use.
Anti-virus utilities scan for computer viruses.
Crashed dick rescuer utility is used to restore disks and corrupted files.
Disk checkers can scan the contents of a hard disk to find files or areas that are corrupted in some way, or were not correctly saved, and eliminate them for a more efficiently operating hard drive.
Disk cleaners can find files that unnecessary to computer operation, or take up considerable amounts of space. Disk cleaner helps the user to decide what to delete when their hard disk is full.
Disk compression utilities can transparently compress/uncompress the contents of a disk, increasing the capacity of the disk.
File managers provide a convenient method of performing routine data management tasks, such as deleting, renaming, cataloging, moving, copying, merging, generating and modifying data sets.
Launcher applications provide a convenient access point for application software.
| Media player lets you watch DVDs, play music and listen to the radio on the Web. Network managers check the computer's network, log events and check data transfer. Registry cleaners clean and optimize the Windows registry by removing old registry keys that are no longer in use. System profilers provide detailed information about the | 
|
software installed and hardware attached to the computer.
Text and Hex Editors modify text or data of a file. These files could be data or an actual program.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-12-27; Просмотров: 644; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!