
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Rotational kinetic energy and moment of inertia
Major Points
1. The definition of moment of inertia, which is a measure of resistance to angular acceleration.
2. The rotational kinetic energy of a rigid body.
3. The definition of torque. The concept of a lever arm.
In previous chapters we were concerned only with translational motion. We now broaden our interest to include the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis of rotation. A rigid body is defined as an object that has fixed size and shape. In other words, the relative positions of its constituent particles remain constant. Although a perfectly rigid body does not exist, it is a useful idealization. By "fixed axis" we mean that the axis must be fixed relative to the body and fixed in direction relative to an inertial frame. When the axis of rotation is also fixed in position, for example, by an axle, as in Fig. 11.1a, the body undergoes pure rotational motion: All particles of the body move in circular paths centered on the axis of rotation. If the axis is not fixed in position, as is the case for a cylinder rolling down an incline (Fig. 11.1b), then it passes through the center of mass. The discussion of general rotation, in which both the position and the direction of the axis change, is quite complex. The only such case we will discuss is that of the gyroscope (spinning top) in the next chapter.
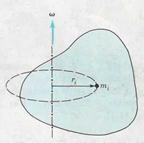
Figure 6.1 shows a rigid body of arbitrary shape rotating about an axis fixed both in position and in direction. The body consists of point particles of mass mi at distances ri from the axis. Note that the ri are the perpendicular distances to the axis, not the distances from an origin. The kinetic energy of the i th particle is 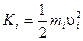 . Since all the particles have the same angular velocity υ i =ω ri, we have
. Since all the particles have the same angular velocity υ i =ω ri, we have 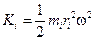 . The total kinetic energy
. The total kinetic energy
|
| FIGURE 6.1 |
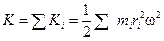
may be written in the form
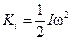 (6.1)
(6.1)
where
Moment of inertia 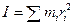 (6.2)
(6.2)
I is called the moment of inertia of the body about the given axis. For rotation about a fixed axis, it may be taken to be a scalar. The value of I depends on the location of the axis, that is, on how the mass of the body is distributed relative to the axis. Thus, a body does not possess a unique moment of inertia; different axes through the body are associated with different moments of inertia.
When 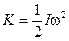 is compared with
is compared with 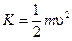 , we see that moment of inertia is analogous to mass. That is, I plays the same role in rotational motion that m plays in translational motion.
, we see that moment of inertia is analogous to mass. That is, I plays the same role in rotational motion that m plays in translational motion.
The moment of inertia of a body is a measure of its rotational inertia, that is, its resistance to change in its angular velocity.
|
| FIGURE 6.2 |
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 448; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!