
КАТЕГОРИИ:
Архитектура-(3434)Астрономия-(809)Биология-(7483)Биотехнологии-(1457)Военное дело-(14632)Высокие технологии-(1363)География-(913)Геология-(1438)Государство-(451)Демография-(1065)Дом-(47672)Журналистика и СМИ-(912)Изобретательство-(14524)Иностранные языки-(4268)Информатика-(17799)Искусство-(1338)История-(13644)Компьютеры-(11121)Косметика-(55)Кулинария-(373)Культура-(8427)Лингвистика-(374)Литература-(1642)Маркетинг-(23702)Математика-(16968)Машиностроение-(1700)Медицина-(12668)Менеджмент-(24684)Механика-(15423)Науковедение-(506)Образование-(11852)Охрана труда-(3308)Педагогика-(5571)Полиграфия-(1312)Политика-(7869)Право-(5454)Приборостроение-(1369)Программирование-(2801)Производство-(97182)Промышленность-(8706)Психология-(18388)Религия-(3217)Связь-(10668)Сельское хозяйство-(299)Социология-(6455)Спорт-(42831)Строительство-(4793)Торговля-(5050)Транспорт-(2929)Туризм-(1568)Физика-(3942)Философия-(17015)Финансы-(26596)Химия-(22929)Экология-(12095)Экономика-(9961)Электроника-(8441)Электротехника-(4623)Энергетика-(12629)Юриспруденция-(1492)Ядерная техника-(1748)
Angular momentum
|
|
|
|
Consider a single particle that has linear momentum p and is located at position r relative to an origin O, as in Fig. 12.2. Its angular momentum ℓ is defined as
Single particle ℓ = r × p (6.8)
Angular momentum is measured with respect to a point, the origin of the position vector r. It is often convenient to express the magnitude of ℓ in terms of the "moment arm," 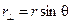 , which is the perpendicular distance from the origin to the line of motion of the particle. Thus,
, which is the perpendicular distance from the origin to the line of motion of the particle. Thus,
Single particle ℓ = rp sin θ = 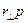 (6.9)
(6.9)
The SI unit of angular momentum is kg·m2/s.
SYSTEM OF PARTICLES
The total angular momentum L of a system of particles relative to a given origin is the sum of the angular momenta of the particles. From Eq. 6.9,
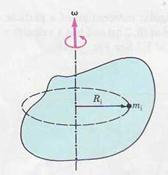
|
| FIGURE 6.10 |
(System of particles) L= ∑ ℓi =∑ r i × p i (6.10)
This sum takes a simple form in the special case of a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. The origin can be chosen at any point on the axis of rotation, which we take to be the z axis. The angular momentum of the i th particle is 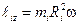 , where Ri is the radius of its circular path. Thus, the z component of the total angular momentum of a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis is
, where Ri is the radius of its circular path. Thus, the z component of the total angular momentum of a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis is
Lz= ∑ ℓiz =∑ 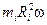
Since the moment of inertia is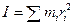 , we have
, we have
(Rigid body, fixed axis) Lz = Iω (6.11)
The subscript z is often dropped. Equation 12.7 is not a vector equation; it represents only the component of the angular momentum along the angular velocity. Note that L = Iω has the same form as p = mv: the product of an inertial property and a speed. Thus, angular momentum is the rotational analog of linear momentum.
|
|
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2014-01-05; Просмотров: 375; Нарушение авторских прав?; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы!